QIAwave RNA Mini Kit (50) icon_0368_ls_gen_eco_friendly-s
Cat no. / ID. 74534
Features
- RNA quality and performance identical to the RNeasy Mini Kit
- Up to 60% less plastic and up to 57% less cardboard compared to the RNeasy Mini Kit
- Reusable Waste Tubes made from 100% post-consumer recycled plastic
- Buffer concentrates that use up to 90% less plastic than our standard buffer bottles
Product Details
The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit is an eco-friendlier version of our standard RNeasy Mini Kit. The kit uses up to 60% less plastic and up to 57% less cardboard than our standard kit and offers waste tubes made from 100% post-consumer recycled plastic that you can reuse throughout the procedure. QIAwave buffers also come as concentrates, reducing the amount of plastic by up to 90% per bottle. To save paper, there are no printed protocols in the kit. Instead, you can download the protocols you need from the resources list or by simply scanning the QR code inside the box lid. So, while the kit packaging and components of our QIAwave Kit may look different, it’s as easy to use as the RNeasy Mini Kit, and the chemistry and performance are identical.
Please be aware that you will need sterile glass bottles to store the reconstituted buffers.
In partnership with My Green Lab, we've also assessed the environmental impact of this kit. My Green Lab ACT (accountability, consistency, and transparency) environmental impact factor labels are designed to evaluate and score products on several sustainability criteria. These include:
- Manufacturing
- Responsible chemical management
- Sustainable content within products and packaging materials
- Disposal of the packaging at the end of life
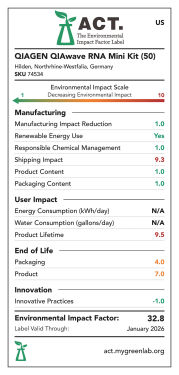
Products are scored from 1 to 10 except for energy and water consumption, which are scored as 1 point per kWh or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact (see figures "QIAwave RNA Mini Kit ACT environmental impact factor label US 50/ 250, EU 50/ 250 and UK 50/ 250").
The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit offers you fast purification of high-quality RNA from cells, tissues, and yeast using silica-membrane RNeasy Mini Spin Columns. Before extraction, you can stabilize tissue samples using RNAprotect Tissue Reagent or Allprotect Tissue Reagent, and to efficiently homogenize your tissue samples, you can use the TissueRuptor II, TissueLyser III or LT system.
The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit can be automated on the QIAcube Connect using the RNeasy Mini Kit protocols.
Performance
The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit gives you highly reproducible yields of total RNA from animal or human cells, animal or human tissues, and yeast (see table “Total RNA yields obtained with RNeasy Mini Spin Columns” and figure " RT-PCR of RNA from as few as 100 cells").
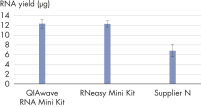
The performance between our QIAwave RNA Mini Kit and RNeasy Mini Kit is identical because the chemistry is the same. We’ve also shown that both kits outperform competitors’ kits (see figure "QIAwave RNA Mini Kit performance").
Total RNA yields obtained with RNeasy Spin Mini Columns
| Source | Average Yield | ||
| Mini | Mini | C | |
| Animal Cells | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| LMH | 1 x 106 | 12 µg | 1.3 µg* |
| HeLa | 1 x 106 | 15 µg | 1.6 µg* |
| COS-7 | 1 x 106 | 35 µg | 3.1 µg* |
| Lymphocytes (unstimulated) | 1 x 106 | 0.5 µg | - |
| Huh7 | - | - | 2.0 µg* |
| Jurkat | - | - | 1.4 µg* |
| Mouse tissue | |||
| Liver | 10 mg | 40 µg | - |
| Lung | 10 mg | 10 µg | - |
| Spleen | 10 mg | 35 µg | - |
| Yeast cells | |||
| S. cerevisiae | 1 x 107 | 25 µg | - |
*Amounts can vary due to developmental stage, growth conditions used, etc.
We have also compared RNA yields obtained with the QIAwave RNA Mini (50) buffer, prepared by pouring or pipetting, and the RNeasy Mini Kit (50) standard buffers. Both methods result in comparable RNA yields as shown in the figure “ Handling buffer concentrates.”
Principle
The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit allows you to efficiently purify total RNA from samples such as:
- microdissected tissues and fine needle aspirates
- milligram amounts of fibrous tissues, including heart and muscle tissue
- small numbers of cells down to a single cell (e.g., FACS sorted cells)
For microdissected FFPE tissues, we recommend using the RNeasy FFPE Kit. The QIAwave Kit simplifies total RNA isolation by combining the stringency of guanidine-isothiocyanate lysis with the speed and purity of silica-membrane purification. The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit also gives you high-quality RNA with minimal copurification of DNA.
Procedure
With the QIAwave Kit, you can purify RNA in four simple steps (see flowchart " QIAwave RNA Mini Procedure").
- Lyse and homogenize samples (see table "Amount of starting material for the QIAwave RNA Mini Kit").
- Add ethanol to the lysate to provide ideal binding conditions.
- Load the lysate onto the RNeasy silica membrane. At this point, the RNA binds to the silica membrane and all contaminants are efficiently washed away. If your downstream applications are sensitive to very small amounts of DNA, you can remove any residual amounts of DNA using a convenient on-column DNase treatment.
- Pure, concentrated RNA is then eluted in water.
In addition to our standard protocol, we also provide a variety of special application protocols.
If you have too many samples to process manually, you can automate the purification process on the QIAcube Connect. The QIAcube Connect allows you fully automate the entire purification procedure for up to 12 samples per run.
QIAwave buffers come as concentrates that you can easily reconstitute by adding water and/or ethanol; please check the handbook for details. QIAwave RNeasy Mini Spin Columns and Waste Tubes come in individual bags and need to be preassembled before you start the protocol. This takes a little extra time, but it does reduce plastic waste.
Amount of starting material for the QIAwave RNA Mini Kit
| Amount of starting material | Mini |
| Cells | 10 to 1 x 107 animal or human cells |
| Tissue | 0.5–30 mg animal or human tissues |
| Yeast | <5 x 107 yeast cells |
The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit can be automated on the QIAcube Connect using the RNeasy Mini Kit protocols.
Applications
RNA purified with QIAwave RNA technology has A260/280 ratios of 1.9–2.1 (measured in 10 mM Tris·Cl, pH 7.5) and is ideal for use in all applications. Downstream applications include:
- RNA-seq
- Quantitative, real-time RT-PCR
- Real-time RT-PCR starting with as little as one cell
- End-point RT-PCR
- Northern, dot, and slot blotting
- Array analysis
- Poly A+ RNA selection
Supporting data and figures
QIAwave RNA Mini Kit (50) ACT environmental impact factor label US.
ACT environmental impact factor labels are designed to evaluate and score products on several sustainability criteria. Products are score 1–10 except for energy and water consumption, which are scored as 1 point per kWh or gallon, respectively. A low score means a lower environmental impact. The QIAwave RNA Mini Kit (50) has a 21.7% lower EIF in the US than the equivalent standard kit, the RNeasy Mini Kit (50).