✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 31314
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- 단 15분 내 컬럼당 최대 300μg의 His-tagged 단백질 정제
- 네이티브 및 변성 조건에서의 정제
- 한 단계로 최대 95%의 균질성 달성
- 신속한 자동 또는 수동 처리를 위한 즉시 사용 가능한 스핀 컬럼
Product Details
Ni-NTA 실리카는 비특이적 소수성 상호작용을 억제하도록 최적화된 거대 다공성 실리카 지지 물질과 Ni-NTA를 결합한 것입니다. Ni-NTA Spin Columns(His-단백질 정제 스핀 컬럼)는 Ni-NTA Spin Kit에 포함되어 있고, 별도로 구입 가능하며, 편리한 마이크로 스핀 형식의 Ni-NTA 실리카를 제공하여 여러 샘플을 병렬적으로 쉽게 준비할 수 있도록 합니다. 엔지니어링 단백질의 기능 스크리닝, 전장 번역 산물을 발현하는 클론 선택, 발현 수준 비교를 위한 간단한 방법을 제공합니다. 각 스핀 컬럼은 최대 300µg의 His-tagged 단백질을 정제할 수 있습니다. 모든 Ni-NTA 매트릭스와 마찬가지로 Ni-NTA 스핀 컬럼은 네이티브 또는 변성 조건에서 원스텝 단백질 정제에 사용할 수 있습니다. Ni-NTA Spin Kit는 His-tagged 단백질의 스핀 정제를 위한 완벽한 키트입니다. It can be automated on the QIAcube Connect (see image " QIAcube Connect").
See figures
Performance
Ni-NTA Spin Columns(His-단백질 정제 스핀 컬럼)도 Ni-NTA Spin Kit에 포함되어 있어 다양한 발현 수준에서(그림 '다양한 발현 수준에서 정제' 참조) 재현 가능한 빠른 자동 정제가 가능합니다(그림 '재현 가능한 자동 정제' 참조).
See figures
Principle
Ni-NTA Spin Columns 및 Ni-NTA Spin Kit를 포함한 QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System은 6개 이상의 히스티딘 잔기인 친화성 태그인 His tag를 포함하는 단백질에 대한 특허받은 Ni-NTA(니켈-니트로트리아세트산) 수지의 뛰어난 선택성을 기반으로 합니다. 이 기술을 사용하면 네이티브 또는 변성 조건하의 모든 발현 시스템에서 거의 모든 His-tagged 단백질의 원스텝 정제가 가능합니다. 니켈 이온의 킬레이트화 부위가 4개인 NTA는 금속 이온과 상호작용할 수 있는 부위가 3개밖에 없는 금속 킬레이트 정제 시스템보다 니켈을 더 단단히 결합합니다. 추가 킬레이트화 부위는 니켈 이온 침출을 방지하고 다른 금속 킬레이트화 정제 시스템을 사용하여 얻은 것보다 더 큰 결합 용량과 더 높은 순도의 단백질 제제를 생성합니다. QIAexpress 시스템은 배큘로바이러스, 포유류 세포, 효모 및 박테리아를 포함한 모든 발현 시스템에서 His-tagged 단백질을 정제하는 데 사용할 수 있습니다.
Procedure
His-tagged 단백질의 정제는 세포 용해, 결합, 세척 및 용출의 4단계로 구성되어 있습니다(그림 'Ni-NTA 단백질 정제 시스템을 사용한 Ni-NTA Spin Column 정제' 참조). QIAexpress 시스템을 사용한 재조합 단백질의 정제는 단백질의 3차원 구조 또는 His tag에 의존하지 않습니다. 이를 통해 희석 용액과 조잡한 용해물로부터 원시 또는 변성 조건에서 원스텝 단백질 정제가 가능합니다. 최대 600μL의 세포 용해물을 Ni-NTA 스핀 컬럼에 로드합니다. 2분간 빠르게 회전하면 tagged 단백질은 Ni-NTA 실리카에 결합하고 태그되지 않은 단백질은 대부분 통과합니다. 세척 단계 후 정제된 단백질은 100~300μL 부피의 온화한 조건(pH를 5.9로 낮추거나 100~500mM 이미다졸을 첨가하는 등)에서 용출됩니다. His tag는 크기가 작고 면역 원성이 거의 없기 때문에 일반적으로는 제거할 필요가 없습니다. 정제된 단백질은 즉시 사용할 수 있습니다. 여러 소규모 발현 배양에서 단백질을 약 30분(수동 절차) 또는 약 60분(자동화된 QIAcube Connect 절차) 내에 정제할 수 있습니다. 수용체, 막 단백질, 봉입체를 형성하는 단백질의 효율적인 용해 및 정제를 위해 강력한 변성제 및 세제를 사용할 수 있습니다. 비특이적으로 결합하는 오염 물질을 효율적으로 제거할 수 있는 시약을 세척 완충액에 첨가할 수 있습니다(표 참조). 정제된 단백질은 경쟁 물질로 100~250mM 이미다졸을 첨가하거나 pH를 낮추어 온화한 조건에서 용출됩니다.
Ni-NTA–His 상호 작용과 호환되는 시약:
- 6M 구아니딘 HCl
- 8M 요소
- 2% Triton X-100
- 2% Tween 20
- 1% CHAPS
- 20mM β-ME
- 10mM DTT
- 50% 글리세롤
- 20% 에탄올
- 2M NaCl
- 4M MgCl2
- 5mM CaCl2
- ≤20mM 이미다졸
- 20mM TCEP
See figures
Applications
Ni-NTA Spin Columns 및 Ni-NTA Spin Kit를 포함한 QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System은 다음을 비롯한 모든 애플리케이션에 적합한 신뢰할 수 있는 원스텝 단백질 정제를 제공합니다.
- 구조적 및 기능적 조사
- 3차원 구조 결정을 위한 결정화
- 단백질–단백질 및 단백질–DNA 상호작용 관련 분석
- 항체 생성을 위한 예방접종
| 특성 | Ni-NTA Spin Columns | Ni-NTA Spin Kit |
| 애플리케이션 | 단백질체학 | 단백질체학 |
| 비드 크기 | 16–24 µm | 16–24 µm |
| 결합 용량 | 스핀 컬럼당 최대 300µg | 스핀 컬럼당 최대 300µg |
| 중력류 또는 스핀 컬럼 | 스핀 컬럼 | 스핀 컬럼 |
| 처리 | 자동/수동 | 자동 |
| 규모 | 소규모 | 소규모 |
| 특수 기능 | 처리량이 적은 스크리닝 | 한 단계로 최대 95%의 균질성 달성 |
| 시작 물질 | 세포 용해물 | 세포 용해물 |
| 지원/매트릭스 | 거대 다공성 실리카 | 거대 다공성 실리카 |
| 태그 | 6xHis tag | 6xHis tag |
Supporting data and figures
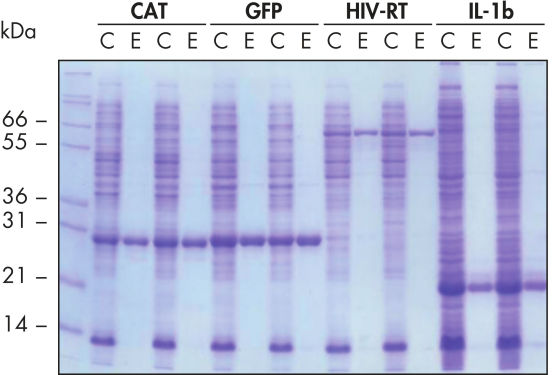
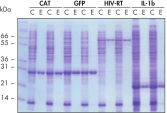
재현 가능한 자동화된 정제.
표시된 단백질은 5mL LB 배양물에서 추출한 정제된 E. coli 세포 용해물로부터 Ni-NTA Spin Columns를 사용하여 네이티브 조건에서 수동 또는 QIAcube의 자동화된 절차로 두 번 정제했습니다. CAT: Chloramphenicol Acetyl Transferase(클로람페니콜 아세틸 전이효소); GFP: Green Fluorescent Protein(녹색 형광 단백질); HIV-RT: Human Immunodeficiency Virus Reverse Transcriptase(인간 면역결핍 바이러스 역전사 효소); IL-1b: Interleukin-1 Veta(인터루킨-1 베타). M: 마커; C: 제거된 용해물(레인당 2μL 로드함); E: 용출 분획물(레인당 3μL 로드함).