✓ Traitement automatique des commandes en ligne 24 h/24 7 j/7
✓ Assistance technique et produits pertinente et professionnelle
✓ Commande (ou réapprovisionnement) rapide et fiable
Cat. No. / ID: 31314
✓ Traitement automatique des commandes en ligne 24 h/24 7 j/7
✓ Assistance technique et produits pertinente et professionnelle
✓ Commande (ou réapprovisionnement) rapide et fiable
Caractéristiques
- Jusqu’à 300 μg de protéines marquées à l’histidine par colonne en 15 minutes seulement
- Purification en conditions natives et dénaturantes
- Jusqu’à 95 % d’homogénéité en une étape
- Colonnes de centrifugation prêtes à l’emploi pour un traitement automatisé ou manuel rapide
Détails produit
La silice Ni-NTA associe le Ni-NTA à un support en silice macroporeuse optimisé pour supprimer les interactions hydrophobes non spécifiques. Avec les Ni-NTA Spin Columns (colonnes de centrifugation pour purification des protéines marquées à l’histidine) du Ni-NTA Spin Kit, qui sont aussi disponibles séparément, la silice Ni-NTA est proposée dans un format pratique de microcentrifugation pour faciliter la préparation de plusieurs échantillons en parallèle. Elles proposent une méthode simple pour le criblage fonctionnel de protéines modifiées, la sélection de clones exprimant des produits de traduction complets et la comparaison des niveaux d’expression. Chaque colonne de centrifugation est capable de purifier jusqu’à 300 µg de protéines marquées à l’histidine. Comme toutes les matrices de Ni-NTA, les Ni-NTA Spin Columns peuvent être utilisées pour la purification des protéines en une étape en conditions natives ou dénaturantes. Le Ni-NTA Spin Kit est un kit complet destiné à la purification par centrifugation des protéines marquées à l’histidine. Il peut être automatisé sur le QIAcube Connect (consultez l’image « QIAcube Connect »).
Voir les illustrations
Performances
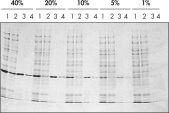
Les Ni-NTA Spin Columns (colonnes de centrifugation pour purification des protéines marquées à l’histidine), également incluses dans le Ni-NTA Spin Kit, permettent une purification automatique, rapide et reproductible (consultez l’illustration « Purification automatique reproductible ») à différents niveaux d’expression (consultez l’illustration « Purification à différents niveaux d’expression »).
Voir les illustrations
Principe
Le QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System, qui comprend les Ni-NTA Spin Columns et le Ni-NTA Spin Kit, est basé sur la remarquable sélectivité de la résine Ni-NTA (Nickel-Acide nitrilotriacétique) brevetée pour les protéines contenant un marqueur d’affinité d’au moins six résidus d’histidine – le marqueur His-tag. Cette technologie permet la purification en une étape de quasiment toutes les protéines marquées à l’histidine à partir de n’importe quel système d’expression en conditions natives ou dénaturantes. Le NTA, qui présente quatre sites de chélation pour les ions nickel, lie le nickel plus étroitement que les systèmes de purification par chélation du métal qui ne présentent que trois sites pour l’interaction avec les ions métalliques. Le site de chélation supplémentaire empêche la lixiviation des ions nickel et offre une plus grande capacité de liaison ainsi que des préparations des protéines d’une pureté supérieure à celle obtenue avec d’autres systèmes de purification par chélation du métal. Le QIAexpress System peut être utilisé pour purifier les protéines marquées à l’histidine à partir de n’importe quel système d’expression, y compris les baculovirus, les cellules de mammifères, les levures et les bactéries.
Procédure
La purification des protéines marquées à l’histidine comprend 4 étapes : lyse cellulaire, liaison, lavage et élution (consultez l’illustration « Purification Ni-NTA Spin Column avec le système de purification des protéines Ni-NTA »). La purification des protéines recombinantes avec le QIAexpress System ne dépend pas de la structure tridimensionnelle de la protéine ou du marqueur His-tag. Cela permet une purification des protéines en une étape en conditions natives ou dénaturantes, à partir de solutions diluées et de lysats bruts. Il est possible de charger jusqu’à 600 μl de lysat cellulaire dans une Ni-NTA Spin Column. Une centrifugation rapide de 2 minutes lie la protéine marquée à la silice Ni-NTA, tandis que la plupart des protéines non marquées sont éliminées. Après l’étape de lavage, les protéines purifiées sont éluées en conditions modérées (par exemple réduction de pH à 5,9 ou ajout de 100 à 500 mM d’imidazole) dans un volume de 100 à 300 μl. En général, l’élimination du marqueur His-tag est inutile, car il est petit et rarement immunogène. Les protéines purifiées sont maintenant prêtes à l’emploi. Les protéines peuvent être purifiées à partir de multiples cultures d’expression à petite échelle en près de 30 minutes (procédure manuelle) ou environ 60 minutes (procédure automatisée avec QIAcube Connect). Vous pouvez utiliser des dénaturants et des détergents puissants pour une solubilisation et une purification efficaces des récepteurs, des protéines membranaires et des protéines qui forment les corps d’inclusion. Les réactifs qui permettent d’éliminer correctement les contaminants de liaison non spécifique peuvent être inclus dans les tampons de lavage (voir le tableau ci-dessous). Les protéines purifiées sont éluées en conditions modérées par l’ajout de 100 à 250 mM d’imidazole comme concurrent ou par la réduction du pH.
Réactifs compatibles avec l’interaction Ni-NTA–His :
- Chlorure de guanidinium 6 M
- Urée 8 M
- Triton X-100 2 %
- Tween 20 2 %
- CHAPS 1 %
- β-ME 20 mM
- DTT 10 mM
- Glycérol 50 %
- Éthanol 20 %
- NaCl 2 M
- MgCl2 4 M
- CaCl2 5 mM
- Imidazole ≤20 mM
- TCEP 20 mM
Voir les illustrations
Applications
Le QIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification System, qui comprend les Ni-NTA Spin Columns et le Ni-NTA Spin Kit, permet une purification fiable en une étape des protéines adaptée à de nombreuses applications, notamment :
- Étude des structures et des fonctionnements
- Cristallisation pour la détermination d’une structure tridimensionnelle
- Dosages impliquant des interactions protéine–protéine et protéine–ADN
- Immunisation aux anticorps produits
| Caractéristiques | Ni-NTA Spin Columns | Ni-NTA Spin Kit |
| Applications | Protéomique | Protéomique |
| Taille de bille | 16–24 µm | 16–24 µm |
| Capacité de liaison | Jusqu’à 300 µg par colonne de centrifugation | Jusqu’à 300 µg par colonne de centrifugation |
| Flux gravitationnel ou colonne de centrifugation | Colonne de centrifugation | Colonne de centrifugation |
| Traitement | Automatisé/Manuel | Automatisé |
| Échelle | Petite échelle | Petite échelle |
| Caractéristique spéciale | Criblage de faible débit | Jusqu’à 95 % d’homogénéité en une étape |
| Matériel initial | Lysat cellulaire | Lysat cellulaire |
| Support/Matrice | Silice macroporeuse | Silice macroporeuse |
| Marqueur | Marqueur 6xHis-tag | Marqueur 6xHis-tag |
Données et illustrations utiles
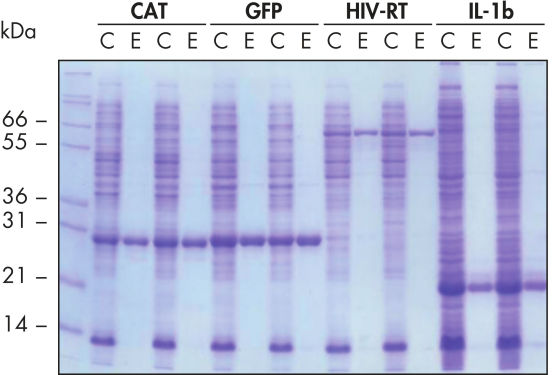
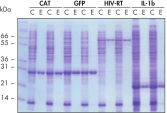
Purification automatique reproductible.
Les protéines indiquées ont été purifiées en double en conditions natives avec les colonnes de centrifugation Ni-NTA à partir de lysats cellulaires d’E. coli clarifiés extraits de 5 ml de cultures LB de façon manuelle ou automatique sur le QIAcube. CAT : chloramphénicol acétyltransférase ; GFP : protéine fluorescente verte ; RT-VIH : transcriptase inverse du virus de l’immunodéficience humaine ; IL-1b : interleukine-1 bêta. M : marqueurs ; C : lysat clarifié (2 μl chargés par voie) ; E : fraction d’élution (3 μl chargés par voie).