qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Assays
がんおよび腫瘍発生において特異的なDNA配列変異の検出用
がんおよび腫瘍発生において特異的なDNA配列変異の検出用
カタログ番号 / ID. 337011
| Popular Products | GeneGlobe ID |
|---|---|
| qBiomarker Somatic Mutation Assay for TP53_43778 | SMPH034467A |
| qBiomarker Somatic Mutation Assay for SF3B1_98000019 | SMPH038660A |
| qBiomarker Somatic Mutation Assay for TP53_43609 | SMPH034567A |
| qBiomarker Somatic Mutation Assay for PDGFRB_99099 | SMPH054591A |
| qBiomarker Somatic Mutation Assay for PDGFRB_96116 | SMPH054586A |
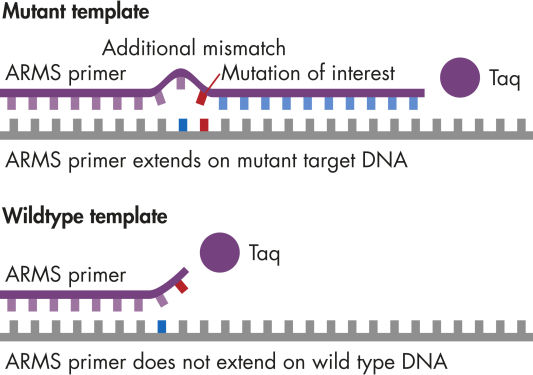
qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Assayは、毒性研究、創薬、がん研究において重要である細胞株または研究サンプルに存在する特異的な配列変異の有無を個々に同定します。変異は、臨床または機能的関連性および患者集団での出現頻度に基づいて、広範な体細胞突然変異のデータベース(例;COSMIC)と査読済み科学文献から選択されています。
新鮮、凍結、または固定されたサンプルからゲノムDNAを分離後、適切なマスターミックス(付属)とqBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Assayが入ったリアルタイムPCRチューブに各サンプルを分注します。また、適切なマスターミックス(付属)と対応するリファレンス遺伝子コピーアッセイの入った別のリアルタイムPCRチューブに各サンプルを分注します。最後に推奨されているサイクリングプログラムを開始します。
サンプルごとに、各突然変異特異的なアッセイと対応するリファレンス遺伝子のコピーアッセイのCT値を、装置のソフトウェアを使用して決定します。その後、この値をエクセルベースのデータ解析テンプレートにペーストし、テストした突然変異を含むサンプルを決定します。
qBiomarker Somatic Mutation PCR Assayは、新鮮、凍結、固定サンプル中に存在する特異的な配列突然変異を迅速かつ正確に個々に同定します。