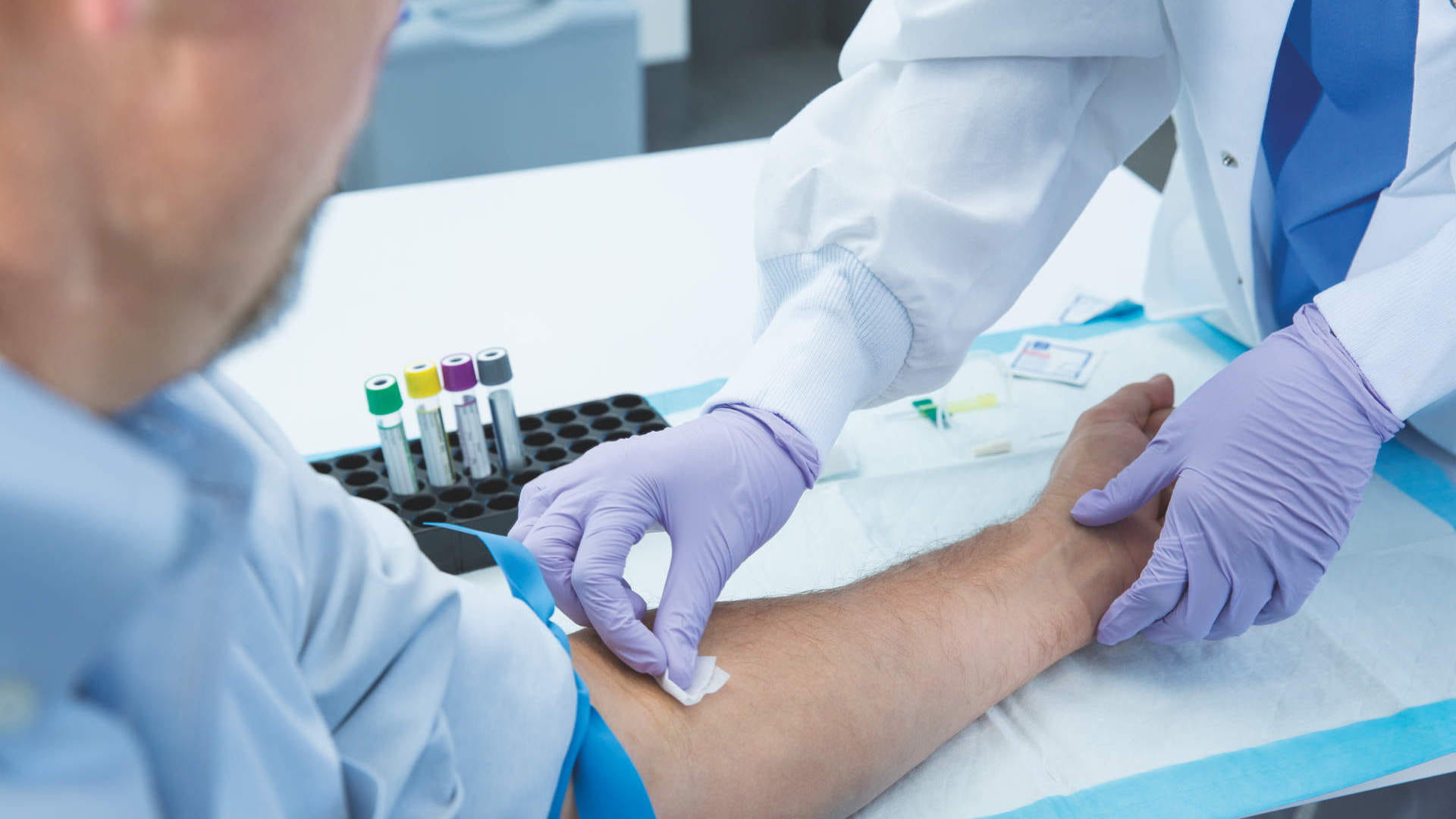
What are the key differences between a TB skin test and a TB blood test?
Two tests are used for tuberculosis infection: the tuberculin skin test (TST) and the interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA), commonly known as the TB blood test.
The TB blood test uses a blood sample to measure the immune response to TB-specific antigens in a laboratory. The TB skin test requires injecting purified TB proteins under the skin and measuring the local swelling 2–3 days later with a ruler.
The TB blood test requires only one visit and is more specific than the TB skin test, reducing false-positive results. The TB skin test requires a minimum of two visits and can cross-react with the common BCG vaccine.
QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus vs. TB skin test
QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus is the world’s leading TB blood test. It’s more accurate than the skin test, unaffected by prior BCG vaccination, and uses a controlled laboratory assay to provide clear and objective results.
Understanding the differences between the skin test and the blood test can help you determine which test to use. It is important to consider which TB test is more accurate and how often each test needs to be performed.
Which is better for your patients, the TB skin test or the TB blood test?
| Test Type | ||
|---|---|---|
Type of test |
Interferon-gamma release assay performed using a whole blood sample | Intradermal injection of purified protein derivative (PPD) tuberculin |
Doctor visits required |
One visit | Two to four visits depending on the testing setting |
Test specificity |
More specific for TB infection than the TST, particularly in BCG-vaccinated patients | Less specific for TB infection than IGRA, particularly in BCG-vaccinated patients |
BCG vaccine and non-specific reactivity |
No false positives from the BCG vaccine and most environmental mycobacteria | False positives can result from the BCG vaccine and environmental mycobacteria |
Test controls |
Positive and negative controls | No test controls |
Test interpretation |
Objective test results Results are interpreted using the measurement of Interferon-gamma in a laboratory |
Subjective test results Results are obtained by measuring local skin induration (swelling) with a ruler |
Test cutoffs |
Single universal test cutoff for all patients | Different test cutoffs for different patients (5 mm, 10 mm, or 15 mm) |
Subject to boosting |
No, not subject to boosting | Yes, a recent TB test may boost subsequent test results |
- QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus (QFT-Plus) Package Insert. 1095849 Rev. 09, Jan 2023.
- US CDC. Updated guidelines for using interferon gamma release assays to detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection – United States 2010. MMWR 59 RR-5.