✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
Cat. No. / ID: 32903
✓ 全天候自动处理在线订单
✓ 博学专业的产品和技术支持
✓ 快速可靠的(再)订购
特点
- C 端 6xHis 标签可确保只纯化全长蛋白
- 用于将表达不良的蛋白质表达为 DHFR 融合的 pQE-16 载体
- 用于将短肽表达为 DHFR 融合的 pQE-16 载体
产品详情
此载体组提供 3 种载体(pQE-16、pQE-60 和 pQE-70),用于表达 C 端 6xHis 标签蛋白,建议用于带有“暂停位点”的开放阅读框,这类位点可能导致提前终止。pQE-60 和 pQE-70 允许编码片段的原始起始密码子取代 pQE 载体中的 ATG,从而保留蛋白的真实 N 端。这两个构建体是通过 PCR 或诱变在插入片段的 ATG 密码子处分别引入 NcoI 和 SphI 限制酶切位点而创建的。pQE-16 允许表达 C 端 6xHis 标记 DHFR 融合蛋白。DHFR(二氢叶酸还原酶)可增强抗原性和稳定性,建议用于表达不良的蛋白质或易被蛋白水解的短肽。由于 DHFR 本身在小鼠和大鼠中几乎没有显示出免疫原性,因此 DHFR 融合蛋白是表位筛选的理想选择。
原理
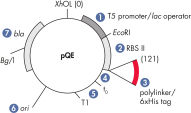
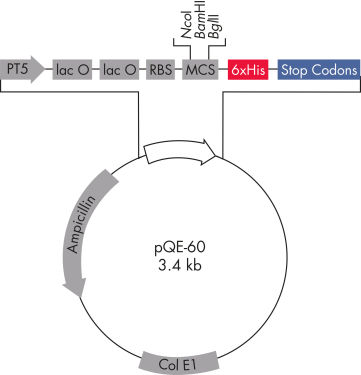
QIAexpress pQE 载体将强大的噬菌体 T5 启动子(由大肠杆菌 RNA 聚合酶识别)与 doublelac 操作子抑制模块相结合,在大肠杆菌中提供严格调控的高水平重组蛋白表达(见图“ QIAexpress pQE 载体”)。存在高浓度的 lac 抑制剂时,蛋白合成被有效阻断,细胞毒性构建体的稳定性得到增强。 pQE 载体可将 6xHis 标签置于重组蛋白的 N 端或 C 端。
| 元素 | 说明 |
| 经过优化的启动子/操作子元素 | 由噬菌体 T5 启动子和两个 lac 操作子序列组成,可提高 lac 抑制剂结合的概率,并确保有效抑制强大的 T5 启动子 |
| 合成核糖体结合位点 RBSII | 用于高效翻译 |
| 6xHis-tag 编码序列 | 多接头克隆区的 5' 或 3' |
| 翻译终止密码子 | 在所有阅读框中,以方便制备表达构建体 |
| 两个强转录终止子 | 来自噬菌体 λ 的 t0 和来自大肠杆菌的 rrnB 操纵子的 T1,用于防止通读转录并确保表达构建体的稳定性 |
| ColE1 复制起始点 | 来自 pBR322 |
| β-内酰胺酶基因 (bla) | 赋予氨苄西林抗药性 |
查看图表
程序
编码目标蛋白的插入片段被克隆到适当的构建体中(有关详细信息,请参阅 QIAexpressionist 手册),并转化为合适的大肠杆菌菌株进行表达。通过添加 IPTG 诱导表达。载体 pQE-TriSystem 构建体可以转化为大肠杆菌,作为穿梭载体用于在昆虫细胞中表达重组蛋白,或转染到哺乳动物细胞中。
应用
QIAexpress 表达系统可提供适合许多应用的高水平蛋白表达,
其中包括:
- 纯化具有构象活性的功能性蛋白
- 在变性条件下进行纯化以生产抗体
- 结晶以确定三维结构
- 涉及蛋白间和蛋白与 DNA 之间相互作用的检测
辅助数据和图表
QIAeexpress pQE 载体。
Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Expression species | 大肠杆菌 |
| In-frame cloning necessary | 是 |
| N- or C-terminal tag | C 端标签 |
| Expression | 体内 |
| Special features | 基于 T5 启动子转录-翻译系统 |
| Tag | 6xHis 标签 |
| Tag removal sequence | 否 |
| All three reading frames provided | 是 |