PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD)
For collection of whole blood samples and stabilization of circulating cell-free DNA (ccfDNA) from plasma and genomic DNA (gDNA) from the nucleated cellular fraction
For collection of whole blood samples and stabilization of circulating cell-free DNA (ccfDNA) from plasma and genomic DNA (gDNA) from the nucleated cellular fraction
Cat. No. / ID: 768165
The PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) is intended for the collection, storage, and transport of human venous whole blood and stabilization of DNA for preparation of circulating, cell-free DNA (ccfDNA) from plasma and genomic DNA (gDNA) from the nucleated cellular fraction.
The PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD), the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit (CE-IVD), and QIAGEN QIAsymphony instrument (CE-IVD) are all CE marked for In Vitro Diagnostic Use according to Regulation (EU) 2017/746 on In Vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices. (See "PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Workflow (CE-IVD)".)
Plasma generated from the whole blood collected into the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) can be used to process ccfDNA, automated with the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit, or manually with the QIAamp DSP Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit. The nucleated cellular fraction or buffy coat remaining after removal of the plasma can be processed for gDNA, automated with the QIAsymphony DSP DNA Mini and Midi Kits for automated extraction, or manual extraction using the QIAamp DSP DNA Blood Mini Kit.
*Only when used in combination with products for In Vitro Diagnostic use.
PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) simplify the collection and processing of whole blood for subsequent purification of circulating, cell-free DNA (ccfDNA) from plasma and genomic DNA (gDNA) from the nucleated cellular fraction. The tube additive is non-crosslinking, free of formaldehyde-releasing substances, stabilizes blood cells and inhibits apoptosis.
Using PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) for whole blood collection, storage and transport helps prevent the release of intracellular DNA into plasma (see " PAXgene Blood ccfDNA stabilization reagent helps prevent release of gDNA into plasma").
Plasma generated from whole blood collected into PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) can be used to process ccfDNA, automated with the PreAnalytiX QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit (CE-IVD) or manually with the QIAamp DSP Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit. The nucleated cellular fraction or buffy coat remaining after removal of the plasma can be processed for gDNA, automated with the QIAsymphony DSP DNA Mini and Midi Kits, or manually with the QIAamp DSP DNA Blood Mini Kit (See "PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Workflow (CE-IVD)").
ccfDNA yields from plasma processed from blood collected into PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) extracted with the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit (CE-IVD) or the QIAamp DSP Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit are similar to plasma from EDTA tubes separated directly after blood draw (See " Relative yield for ccfDNA from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) plasma processed automated or manually compared to EDTA tube plasma at Day 0."). However, in contrast to unstabilized EDTA, blood drawn into PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes have stable ccfDNA levels for up to 10 days at temperatures up to 25°C, 7 days at temperatures up to 30°C or 3 days at temperatures up to 37°C (Note: Do not store blood-filled tubes below 2°C), because DNA release from cells lysing or undergoing apoptosis is inhibited (See " Minimization of DNA release into plasma from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).") and ccfDNA is preserved (See " Preservation of ccfDNA yield in plasma from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).").
Genomic DNA in the nucleated cellular fraction is preserved and can be isolated with high purity, yield, and integrity (See " Yield, purity and integrity of gDNA from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD)."). Thus, blood samples can be transported and stored within the specified temperature and duration to process plasma later (see technical note "Sample Transportation Study (Summer Profile)").
Plasma and nucleated cellular fraction generated from whole blood collected into PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes are stable at room temperature for at least 3 days, at refrigerated temperature for at least 7 days and can be stored for long-term frozen at -20°C or -80°C (For latest update see technical note "Plasma and Nucleated Cellular Fraction Stability Study").
Pre-analytical steps including handling, storage, processing and documentation of verification and validation studies of PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube were conducted in accordance with ISO 20186-2:2019 and ISO 20186-3:2019: Molecular in vitro diagnostic examinations — Specifications for pre-examination processes for venous whole blood — Part 2: Isolated genomic DNA and — Part 3: Isolated circulating cell free DNA from plasma.
Stabilization characteristics have been shown to be robust against elevated level of endogenous, potentially interfering substances, underfilling and inappropriate mixing (See technical note "Tube Robustness Study").
Both ccfDNA and gDNA yields are high-quality and are compatible for downstream analytical PCR assays, including user-validated methylation-based PCR, and next-generation sequencing (NGS) molecular test methods (See " Quality Parameters demonstrate ccfDNA isolated from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) compatibility with NGS-based test methods.").
 PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Workflow (CE-IVD)
PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Workflow (CE-IVD)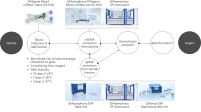 Relative yield for ccfDNA from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) plasma processed automated or manually compared to EDTA tube plasma at Day 0.
Relative yield for ccfDNA from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) plasma processed automated or manually compared to EDTA tube plasma at Day 0.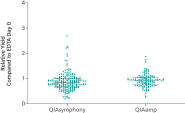 Minimization of DNA release into plasma from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).
Minimization of DNA release into plasma from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).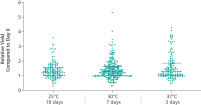 Preservation of ccfDNA yield in plasma from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).
Preservation of ccfDNA yield in plasma from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).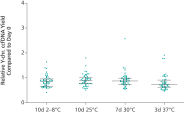 Yield, purity and integrity of gDNA from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).
Yield, purity and integrity of gDNA from blood samples stored in the PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD).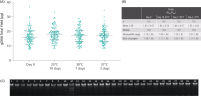 Quality parameters demonstrate ccfDNA isolated from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) compatibility with NGS based test methods.
Quality parameters demonstrate ccfDNA isolated from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) compatibility with NGS based test methods.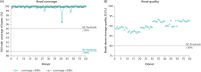
The PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) is intended for the collection, storage, and transport of human venous whole blood and stabilization of DNA for preparation of circulating, cell-free DNA (ccfDNA) from plasma and genomic DNA (gDNA) from the nucleated cellular fraction. The tube contains an additive that keeps blood from coagulating and inhibits apoptosis via a non-crosslinking formaldehyde-free stabilization solution. This helps prevent the release of intracellular DNA into the plasma and maintains constant ccfDNA levels during sample transport and storage before processing.
(For details, see "PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) Instructions for Use")
Blood is collected under a standard phlebotomy protocol into a closed, evacuated tube that contains a proprietary ccfDNA stabilization additive. Whole blood samples can be stored 10 days at temperatures up to 25°C, 7 days at temperatures up to 30°C, or 3 days at temperatures up to 37°C. Do not store blood-filled tubes below 2°C.
Centrifugation of blood collected into a PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube at room temperature (15–25°C) for 15 minutes at 1,600–3,000 × g leads to separation of plasma and nucleated cellular fraction. The cellular fraction includes a buffy coat, a leukocyte and platelet rich layer, and a red blood cell fraction. Plasma is removed after the first centrifugation into a secondary tube. For ccfDNA isolation, the plasma is centrifuged again for 10 minutes at 1,600–3,000 × g. As an alternative after a first centrifugation for 15 minutes at 3,000 × g, the tube can be directly placed on the QIAsymphony SP instrument for automated ccfDNA extraction using the primary tube handling protocol of the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit (applies to 3,000 × g only) (See " Impact of different plasma processing protocols on ccfDNA yield.").
After removal of the plasma, the remaining nucleated cellular fraction can be used to isolate gDNA.
ccfDNA purified from plasma generated from whole blood collected into PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) and purified using the QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit (CE-IVD) or QIAamp DSP Circulating NA Kit can be used in a wide range of downstream applications, including:
PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tube (CE-IVD) is for in vitro diagnostic use.
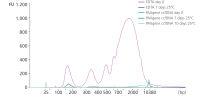
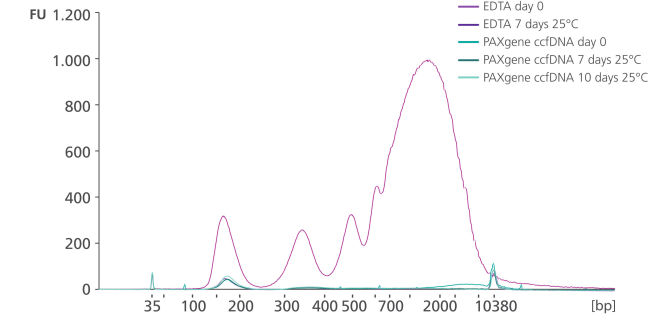
Whole blood was stored in EDTA tubes or PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD). ccfDNA was extracted from the plasma immediately following blood collection (Day 0) and after 7- or 10-days storage at 25°C. Eluate (1 µL) was analyzed using the Agilent High Sensitivity DNA Kit. After 7 days storage, plasma from EDTA tubes showed an increase in apoptotic gDNA fragments, whereas plasma from PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Tubes (CE-IVD) showed a ccfDNA profile comparable to day 0.
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Tube size | 16 x 100 mm |
| Draw volume | 10 mL |
| Additive/concentration | Additive 1.5 mL |
| Stabilization | Length of stabilization of whole blood: 2–37°C for up to 3 days; 2–30°C for up to 7 days; 2–25°C for up to 10 days; Do not store blood-filled tubes below 2°C. ccfDNA stabilization in plasma in secondary tube: 2–25°C for up to 3 days, 2–8°C for up to 7 days, Plasma can be stored frozen at −20 or −80°C for at least 1 year (long term study ongoing) and is robust against at least three freeze/thaw cycles. Stabilization of gDNA in nucleated cellular fraction post-centrifugation: 15–25°C for up to 3 days, 2–8°C for up to 7 days; Nucleated cellular fraction can be stored frozen at −20 or −80°C for at least 1 year (long-term study ongoing) and is robust against at least three freeze/thaw cycles. |
| Closure type/color | Pearl white BD Hemogard/Blue stopper |
| Quantity | 100 tubes/case |
| Shelf life | 15 months from date of manufacture |
| Fractions isolated | ccfDNA isolation from plasma: Automated with the PreAnalytiX QIAsymphony PAXgene Blood ccfDNA Kit using the QIAGEN® QIAsymphony® SP instrument (including primary tube handling); Manual with the QIAGEN QIAamp® DSP Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit. |
| Fraction isolated | gDNA isolation from nucleated cellular fraction or buffy coat: Automated with the QIAGEN QIAsymphony DSP DNA Mini and Midi Kits using the QIAsymphony SP instrument; Manual with the QIAGEN QIAamp DSP DNA Blood Mini Kit. |