Cat. No. / ID: 34362
Eigenschaften
- Exprimierte His-tags, optimiert für die Entfernung durch das TAGZyme Enzym
- Effiziente Entfernung von His-tags: > 95 % in nur 30 Minuten bei 37 °C
- Hohe Expressionslevel von Proteinen mit N-terminalem His-tag
- Hochreine Endprodukte
- Vollständige Entfernung von Verunreinigungen durch das Ni-NTA-Verfahren
Angaben zum Produkt
TAGZyme DAPase Enzyme enthält ausreichend Enzym für die hochspezifische und effiziente Entfernung von His-tags in bis zu 10 mg Protein mit His-tag. Das TAGZyme System kann zur Entfernung von His-tags bei Proteinen verwendet werden, die einen mit dem TAGZyme Vektor pQE-2 exprimierten intrinsischen DAPase-Stopppunkt enthalten.
Leistung
TAGZyme DAPase Enzyme entfernt effizient Dipeptide sequenziell von N-terminalen His-tags bis zu dem mit dem TAGZyme pQE-2-Vektor exprimierten „Stopppunkt“.
Prinzip
Rekombinante Proteine mit His-tag sind zu wertvollen Werkzeugen für Struktur- und Funktionsuntersuchungen von Proteinen geworden. Aufgrund der geringen Größe und Immunogenität des His-tags muss dieser normalerweise nicht entfernt werden. Für einige Anwendungen, beispielsweise für Strukturbestimmungen mittels Röntgenstrahlen oder NMR sowie für die Herstellung von Therapeutika, sollte das Proteinprodukt jedoch keine vektorbedingten Aminosäuren enthalten.
Der TAGZyme pQE-2-Vektor eignet sich für Proteine mit einem intrinsischen DAPase-Stopppunkt.
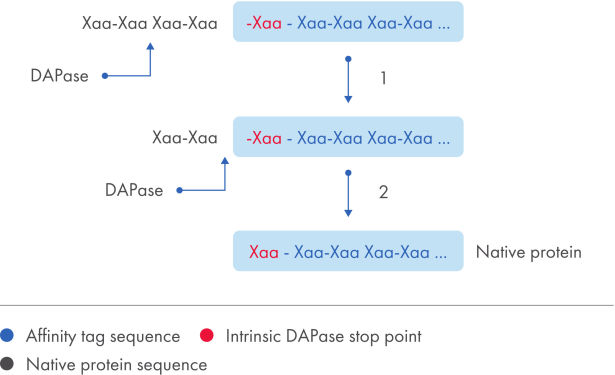
Das TAGZyme System entfernt hochspezifisch und hochwirksam die N-terminalen His-tags rekombinanter Proteine. Mit dem Enzym DAPase werden nacheinander Dipeptide vom N-Terminus des aufgereinigten Proteins mit His-tag abgespalten (siehe Abbildung „His-tag-Entfernung“”). Sobald das Enzym einen “Stopppunkt” erreicht, d. h. ein Aminosäuremotiv, das nicht als Substrat dienen kann, wird der Verdauprozess gestoppt (siehe Tabelle „DAPase-Stopppunkte“).
DAPase-Stopppunkte
| Aminosäure | Sequenz* DAPase-Stopppunkt (↓) |
|---|---|
| Lysin (Lys, K) | Xaa-Xaa...Xaa-Xaa ↓ Lys-Xaa... |
| Arginin (Arg, R) | Xaa-Xaa...Xaa-Xaa ↓ Arg-Xaa... |
| Prolin (Pro, P) | Xaa-Xaa...Xaa-Xaa ↓ Xaa-Xaa-Pro-Xaa... |
| Prolin (Pro, P) | Xaa-Xaa...Xaa-Xaa ↓ Xaa-Pro-Xaa-Xaa... |
| Glutamin (Gln, Q)† | Xaa-Xaa...Xaa-Xaa ↓ Gln-Xaa... |
| Isoleucin (Ile, I) | Xaa-Xaa...Xaa-Xaa ↓ Xaa-Ile-Xaa-Xaa... |
Abbildungen ansehen
Verfahren
Bei rekombinanten Proteinen mit intrinsischen Stopppunkten ermöglicht die Expression mit dem TAGZyme pQE-2-Vektor die vollständige und effiziente Entfernung des N-terminalen His-tags unabhängig von der Klonierungsstelle des DNA-Inserts (siehe Abbildung „His-tag-Entfernung“). Nach der Inkubation mit dem DAPase-Enzym wird das Reaktionsgemisch einer subtraktiven immobilisierten Metall-Affinitätschromatographie (IMAC) mit einer Ni-NTA-Matrix unterzogen (siehe Abbildung „Aufreinigung von Tag-freien Proteinen“). His-tag-Fragmente und das TAGZyme DAPase-Enzym (das einen C-terminalen 6xHis-tag trägt) binden an die Matrix, und aus der Durchflussfraktion wird reines, Tag-freies Zielprotein gewonnen.
Abbildungen ansehen
Anwendungen
Das TAGZyme System bietet eine spezifische Spaltung, den Einsatz rekombinanter Reagenzien und die vollständige Entfernung aller Verunreinigungen und ist damit die Methode der Wahl für die Herstellung His-tag-freier Proteine für Anwendungen wie:
- Bestimmung der Proteinstruktur durch NMR oder Röntgenkristallographie
- Herstellung therapeutischer Proteine
Ergänzende Daten und Abbildungen
His-tag-Entfernung.
Schematische Zusammenfassung der Gesamtstrategie für die Spaltung mit TAGZyme Enzymen. Das Enzym DAPase spaltet einen N-terminalen His-tag von einem Protein, das einen natürlichen Stopppunkt enthält, um das fertige Zielprotein zu erhalten.