✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 150343
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- WGA from single cell material with complete genome coverage
- Unbiased amplification of genomic loci due to MDA technology
- Optimized for use with new technologies, including NGS
- Consistent yields of up to 40 µg (average product length >10 kb)
- Novel tool for cancer research, stem cell research, or metagenomics
Product Details
DNA sequence analysis and genotyping of biological samples using innovative instrumentation, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) platforms, is often limited by the small amount of sample available. The REPLI-g Single Cell Kit is specially designed to uniformly amplify genomic DNA from single cells (1 to <1000 bacterial or tumor cells) or purified genomic DNA with complete genome coverage. Additional protocols are also available for use with fresh or dried blood or fresh or frozen tissue. Dedicated buffers and reagents undergo a unique, controlled decontamination procedure to avoid amplification of contaminating DNA, ensuring highly reliable results every time. Accurate amplification of genomes with negligible sequence bias and no genomic drop-outs is achieved with innovative Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) technology. In contrast to PCR-based WGA technologies, high fidelity rates are increased up to 1000-fold, avoiding costly false positive or negative results.
Performance
Complete genome coverage, highly suited for NGS and other downstream applications
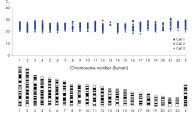
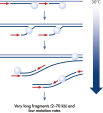
DNA amplified using the REPLI-g Single Cell Kit has an average product length of >10 kb and maximized genome coverage. It has been tested with, and is highly suited for, numerous downstream analyses including next-generation sequencing (NGS), array comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH), and real-time PCR-based applications (see Table 2). Since there is no requirement for a separate PCR-based amplification step, REPLI-g whole genome amplification and library preparation requires less hands-on time and results in longer read-lengths than PCR-based methods (see figure " Next-generation sequencing using REPLI-g amplified DNA requires less hands-on time and generates more sequence information than PCR-based methods"). High-quality, comparable NGS results showing a high percentage of sequence coverage and very low error rates are achieved with both purified genomic DNA or REPLI-g Single Cell amplified DNA, including when starting from just a single bacterial cell (see figure “ Comparable NGS results”). These finding are underscored by a comprehensive analysis of a wide range of markers covering all human autosomal chromosomes and the X chromosome, with 3 different independent experiments demonstrating that DNA is successfully amplified from all areas of the genome without a single drop-out (see figure “ Complete genome coverage”).
| Sample material (cells/DNA) | Research area |
|---|---|
| Human/animal | Biomarker research (SNPs, mutations, CNVs) |
| Stem cell research | |
| Analysis of circulating fetal cells | |
| Mosaicism studies | |
| Genetic predisposition studies | |
| Typing of transgenic animals | |
| Cancer | Somatic genetic variant analysis |
| Tumor progression | |
| Tumor stem cells/evolution | |
| Analysis of circulating tumor cells | |
| Bacteria | Metagenomic studies |
| Pathogen analysis | |
| Microbial genotyping | |
| Plants* | Stomata research |
| Pollen analysis |
The REPLI-g Single Cell Kit outperforms kits from other suppliers
PCR-based WGA methods, as generally used by other suppliers, result in short fragments terminated with PCR primer sequences that may affect downstream processes (e.g., next-generation sequencing; see figure " Next-generation sequencing using REPLI-g amplified DNA requires less hands-on time and generates more sequence information than PCR-based methods"). PCR-based WGA can lead to error-prone amplification that results in, for example, single base-pair mutations, STR contractions, and expansions, and also leads to biased and underrepresented loci due to the use of the low-fidelity enzyme Taq DNA polymerase. In contrast, the REPLI-g Single Cell Kit provides highly uniform amplification across the entire genome, with minimal locus bias during amplification. Four WGA kits, 2 utilizing MDA technology, including the REPLI-g Single Cell Kit, and 2 PCR-based methods, were tested for sequence representation and locus dropout using the single cell amplification protocols specific for each kit. Unlike with the REPLI-g Single Cell Kit, single cells analyzed using kits from other suppliers often failed in complete and unbiased sequence representation (see figure “ Unbiased DNA amplification from a single cell”).
See figures
Principle
The REPLI-g Single Cell Kit includes REPLI-g sc Polymerase, an optimized formulation of the innovative, high-fidelity enzyme Phi 29 polymerase, to amplify complex genomic DNA using Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) technology, along with gentle alkaline incubation to ensure very low DNA fragmentation or generation of abasic sites. It is specifically designed to provide high yields of amplified DNA from single cells, such as isolated tumor cells or bacteria (see Table 1). In addition, it can be used with various clinical and non-clinical research samples and with purified genomic DNA, while additional protocols are available for use with fresh or dried blood and fresh or frozen tissue. Typical DNA yields consistently reach 40 µg, regardless of the starting quantity of template, meaning subsequent genetic analyses can proceed without additional measurement of DNA concentration. The average product length of over 10 kb and complete genome coverage ensures that DNA amplified with the REPLI-g Single Cell Kit is highly suited for numerous downstream applications, including next-generation sequencing (NGS), array-based comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH), Pyrosequencing, and real-time PCR analysis (Table 2).
| Application | Instrumentation |
|---|---|
| Whole genome sequencing | Next-generation sequencing platforms† |
| Exome sequencing | |
| SNP genotyping arrays | Array platforms† |
| Array CGH | |
| qPCR/PCR technologies | Real-time PCR/PCR cyclers† |
| Sanger sequencing | Capillary sequencers† |
| Pyrosequencing | PyroMark (QIAGEN) |
Amplification principle
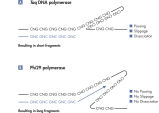
The REPLI-g Single Cell Kit uses isothermal genome amplification, termed Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA), which involves the binding of random hexamers to denatured DNA, followed by strand displacement synthesis at a constant temperature with an optimized form of the enzyme Phi 29 polymerase, which has exceptionally strong strand displacement properties. Additional priming events occur on each displaced strand that serve as a template, enabling generation of high yields of amplified DNA (see figure “ Multiple Displacement Amplification (MDA) technology”). Phi 29 polymerase, a phage derived enzyme, is a DNA polymerase with 3'→5' prime exonuclease activity (proofreading activity) that delivers up to 1000-fold higher fidelity compared to Taq DNA polymerase. Supported by the unique, optimized REPLI-g Single Cell buffer system, Phi 29 polymerase easily solves secondary structures such as hairpin loops, thereby preventing slipping, stoppage, and dissociation of the polymerase during amplification. This enables the generation of DNA fragments up to 100 kb without sequence bias (see figure " Unbiased amplification with Phi 29 polymerase”).
Cell lysis and alkaline denaturation of DNA
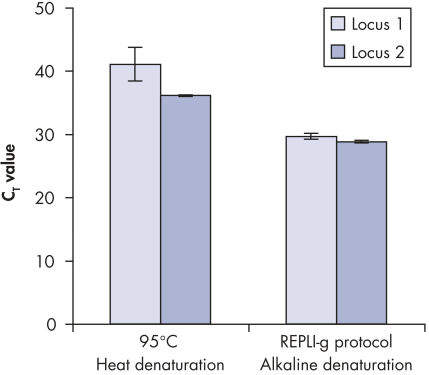
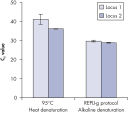
Genomic DNA must be denatured before use in enzymatic amplification procedures, which is often accomplished using harsh methods such as incubation at elevated temperatures (heat incubation) or increased pH (chemical alkaline incubation). The REPLI-g Single Cell Kit uses gentle alkaline incubation, allowing cell lysis and uniform DNA denaturation of gDNA with very low DNA fragmentation or generation of abasic sites. This results in amplified DNA with very high integrity, and maximizes the length of amplified fragments so that genomic loci and sequences are uniformly represented (see figure " Effect of heat and alkaline denaturation on loci representation").
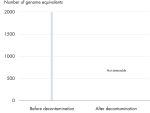
Effective elimination of detectable DNA contamination
All REPLI-g Single Cell Kit components undergo a unique, controlled decontamination procedure to ensure elimination of all REPLI-g amplifiable contaminating DNA. Buffers and reagents are exposed to UV radiation by an innovative and standardized procedure to ensure the absence of any detectable residual contaminating DNA (see figure “ Innovative decontamination procedure”). Following UV treatment, the kits undergo stringent quality control to ensure complete functionality.
See figures
Procedure
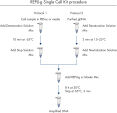
Simple, one tube procedure
The REPLI-g Single Cell Kit uses a simple and reliable method to achieve accurate genome amplification from single cells or limited samples. The easy reaction set-up and very low handling time of approximately 15 minutes makes this a straightforward and reliable method (see figure “ REPLI-g Single Cell Kit procedure”). Dedicated buffers and reagents have been developed to deliver high yields of DNA from single cells, limited tissue material, and purified DNA, with complete sequence representation and unbiased amplification (Table 3). REPLI-g amplified DNA can be stored long-term at –20°C with no negative effects (see figure " Consistent long-term stability").
| Kit component | Advantages |
|---|---|
| REPLI-g sc Polymerase | Long fragments up to 70 kb |
| 1000-fold higher fidelity than Taq | |
| Complete sequence representation | |
| Homogeneous amplification for all loci | |
| REPLI-g sc Reaction Buffer‡ | Optimized for unbiased amplification and representation of all loci |
| Buffer DLB (lysis and denaturation) | Efficient preparation for amplification |
| Non-DNA damaging process | |
| UV decontamination procedure | Ensures elimination of detectable residual DNA contamination |
See figures
Applications
DNA amplified with the REPLI-g Single Cell Kit can be used in a variety downstream applications, including:
- Next-generation sequencing
- SNP genotyping with TaqMan primer/probe sets
- qPCR- and PCR-based mutation detection
- STR/microsatellite analysis
- Sanger sequencing
- Pyrosequencing
- Array technologies, such as comparative genomic hybridization (aCGH)
Learn more about our single cell products by visiting our Single Cell Resource.
Supporting data and figures
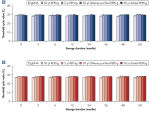
Effect of heat and alkaline denaturation on loci representation.
Effect of heat and alkaline denaturation on loci representation.