✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 335925
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Pan-bacterial 5S/16S/23S rRNA removal from fragmented or full-length RNA for metatranscriptomics studies
- Novel RNA removal mechanism that doesn't involve hybrid capture or enzymatic digestion
- Combine with QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA HMR for ribosomal RNA removal from human, mouse and rat samples for host-microbe studies
- Compatible with QIAGEN, Illumina, NEB and KAPA stranded RNA-seq library preparation kits
- In-silico design predicts blocking of >95% of all 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA database sequences
Product Details
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S Kits use a novel method to remove highly abundant bacterial 5S/16S/23S rRNA from your RNA-seq library. QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S was specifically designed for complex community microbial samples from soil, water, stool and sludge, which have numerous and diverse bacterial populations. The rRNA coverage provided by this kit is based on SILVA 16S sequences (nearly 600,000 entries), SILVA 23S sequences (nearly 170,000 entries) and 5S rRNA database sequences (over 7200 entries), and in-silico modeling shows coverage of >95% of all known 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA sequences.
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S has been tested with QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB RNA-seq library kits and is compatible with all major methods of RNA-seq library preparation. The simple 14-minute protocol and bead cleanup integrates seamlessly with all common RNA-seq library kits, and can be used on fragmented or full-length (non-fragmented) RNA.
For removal of human, mouse, rat and other mammalian rRNA, please see our QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA HMR Kits.
Also, check out our QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits for robust RNA-seq library preparation.
Design your own custom QIAseq FastSelect pools to remove any RNAs you wish from your RNA-seq library – take a look at our QIAseq FastSelect Custom RNA Removal Kits.
Want to try this solution for the first time? Request a trial kit to evaluate.
Performance
In accordance with QIAGEN’s ISO-certified Quality Management System, each lot of the QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S Kit is tested against predetermined specifications to ensure consistent product quality.
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S Kits provide robust rRNA removal from a variety of sample types.
See figures:
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from gut community sample
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from bacterial community (28 strains)
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from bacterial community: mapping analysis (28 strains)
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S Kits deliver highly efficient and reproducible rRNA removal.
See figures:
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust, reproducible rRNA removal from gut microbiome
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust, reproducible rRNA removal from gut microbiome: gene expression results
Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S
Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: gene expression results
Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: gene expression results (100 ng, 1 µg)
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S Kits demonstrated highly efficient removal of rRNA and superior performance compared to alternative methods.
See figures:
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: rRNA removal
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: sequencing reads
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: total reads mapped to rRNA
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S Kits are compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits.
See figures:
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB: gene detection
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB: gene expression
See figures
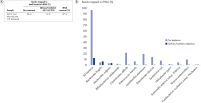 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from bacterial community (28 strains)
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from bacterial community (28 strains)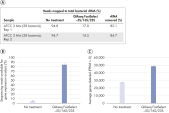 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from bacterial community: mapping analysis (28 strains)
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust rRNA removal from bacterial community: mapping analysis (28 strains) QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust, reproducible rRNA removal from gut microbiome
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust, reproducible rRNA removal from gut microbiome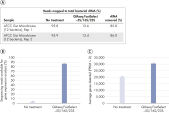 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust, reproducible rRNA removal from gut microbiome: gene expression results
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: robust, reproducible rRNA removal from gut microbiome: gene expression results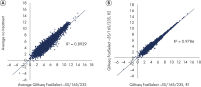 Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S
Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S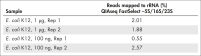 Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: gene expression results
Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: gene expression results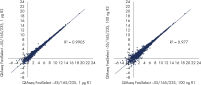 Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: gene expression results (100 ng, 1 µg)
Reproducible rRNA removal from E. coli K12 using QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S: gene expression results (100 ng, 1 µg)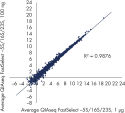 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: rRNA removal
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: rRNA removal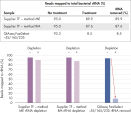 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: sequencing reads
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: sequencing reads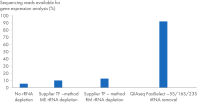 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: total reads mapped to rRNA
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S vs. other methods: total reads mapped to rRNA QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB: gene detection
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB: gene detection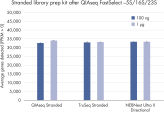 QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB: gene expression
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is compatible with a wide range of RNA-seq library kits, including QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB: gene expression
Principle
Used after bacterial RNA extraction, QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S is a pan-bacterial rRNA removal kit designed to remove 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA from complex bacterial community samples. Our comprehensive rRNA removal reagent has been designed using 16S (nearly 600,000 entries), 23S (nearly 170,000 entries) and 5S rRNA sequences (over 7200 entries). In-silico modeling predicts >95% rRNA removal of all known 5S, 16S and 23S rRNA sequences.
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S can accommodate RNA amounts ranging from as little as 20 ng to 1 µg, with consistently high performance, and is compatible with low-quality, highly fragmented or high-quality full-length RNA. Since QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S does not use enzymatic digestion or hybrid-capture procedures, the fast, simple workflow results in reliable rRNA removal and high reproducibility in downstream applications.
Procedure
Most RNA removal or depletion strategies associated with RNA-seq library construction are sample pre-treatments involving hybrid-capture or enzymatic removal of unwanted RNA. Our unique QIAseq FastSelect procedure is significantly faster and is compatible with most RNA-seq library kits. QIAGEN FastSelect –5S/16S/23S has been tested with QIAGEN, Illumina and NEB stranded RNA-seq library kits.
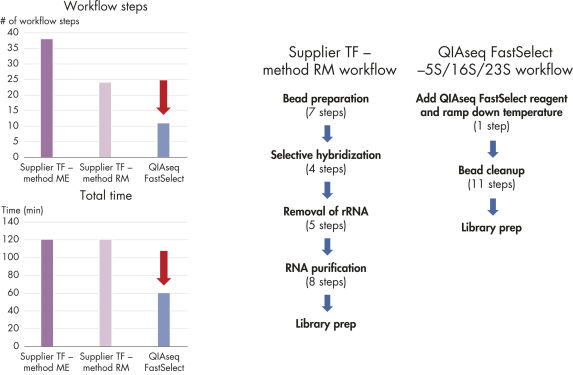
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S seamlessly integrates with your existing RNA-seq library preparation, providing RNA removal in a single, 14-minute step, which is followed by bead cleanup (figure QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S workflow). Prior to RNA heat fragmentation (which is optional and dependent upon the library preparation kit and sample type), QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S removal reagent is directly combined with total RNA and fragmentation buffer. After optional fragmentation, the reaction temperature is stepwise cooled from 75°C to 25°C over 14 minutes, followed by a bead cleanup. The RNA is then ready for reverse transcription. This is dramatically faster than other RNA depletion methods, which require more than 25 steps and approximately 2 hours to complete (figure Bacterial rRNA depletion: alternative products vs. QIAseq Fast Select –5S/16S/23S).
See figures
Applications
QIAseq FastSelect –5S/16S/23S delivers rapid, reliable rRNA removal for bacterial isolates, as well as complex bacterial communities.
Supporting data and figures
Bacterial rRNA depletion: alternative products vs. QIAseq Fast Select