✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 1102308
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Optimal conversion of cfDNA at every step from plasma to NGS library through highly efficient ligation chemistry
- Go directly from eluant to library prep without quantification using a protocol supporting the widest range of cfDNA input (1–100ng)
- Generate PCR-free libraries from 10 ng of cfDNA
- Minimize PCR bias by the use of high-fidelity amplification reagents
- Reduce cross-contamination risk with pre-dispensed plate-based adapters for up to 96 samples/NGS run
Product Details
QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kits provide an optimized solution for cfDNA analysis using any NGS platform from Illumina or Ion Torrent. Kits enable optimal conversion of cfDNA at every step – from plasma to NGS library – and allow sensitive detection of even the rarest variants, providing you with the highest confidence in your results.
Need a quote for your research project or would you like to discuss your project with our specialist team? Contact Us
Performance
Designed for cfDNA
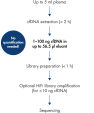
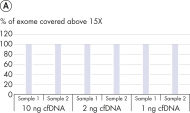
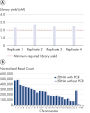
The QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One protocol is specially optimized for cfDNA and generates sequencer-ready NGS libraries from plasma in less than 3 h (see figure " Designed for any NGS-based cfDNA research"). It uniquely combines cfDNA extraction from plasma with library preparation chemistry in a way that avoids sample loss, while ensuring optimal sample conversion at every step. This results in very uniform whole genome or whole exome coverage (see figure " Highly uniform coverage").
Optimal conversion rate of cfDNA to NGS library
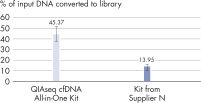
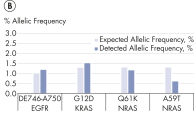
High-efficiency adapter ligation chemistries in the QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kit provide superior cfDNA conversion rates when compared to other suppliers (see figure " Superior conversion rate of cfDNA molecules to NGS library"). This allows highly sensitive detection of mutations down to 1% allelic fractions (see figure " Reliable detection of very rare variants"), making it possible to identify even the rarest variants and have confidence in your cfDNA findings.
Minimal bias through PCR library amplification
Enzyme formulations and buffers optimized for cfDNA yield sufficient library concentrations and allow PCR-free preparation of NGS libraries that are compatible with Illumina sequencers from just 10 ng of isolated cfDNA (see figure " Low error rates and high accuracy in workflows with and without PCR. If starting with less than 10 ng cfDNA, libraries can be amplified using the HiFi PCR master mix, a high-fidelity master mix that minimizes PCR bias, also included with the kit.
For library preparation for Ion Torrent sequencers, we recommend library amplification using the HiFi PCR master mix (included with the kit) prior to sequencing regardless of the sample input amount to enrich for correct adapter-ligated library molecules.
Flexibility with cfDNA extraction method without loss of samples or reduction in data quality
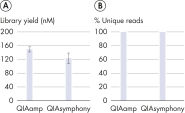
"The QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kit leverages QIAamp Mini Columns for manual cfDNA extraction. Tailored towards high-throughput laboratories, the QIAseq cfDNA Library Kit offers stand-alone cfDNA library prep chemistry for automated cfDNA extraction solutions. Without any compromise on library yield and data quality, labs can transition from manual to automated cfDNA extraction or vice versa (see figure "Equivalent results with manual and automated extraction").
See figures
Principle
Specially developed and optimized for cfDNA samples, the QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kit is a unique solution for NGS-based liquid biopsies. By combining cfDNA extraction and library preparation, the QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kit ensures optimal sample conversion to maximize data yield and confidence in your results. Market-leading QIAGEN extraction technologies ensure highly selective isolation of cfDNA from plasma. High adapter ligation efficiencies guarantee maximal conversion rates of sample to NGS library and allow PCR-free workflows from as little as 10 ng cfDNA (Illumina sequencers). >
Procedure
The QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One workflow consists of two major steps: extraction of cfDNA from plasma and library preparation for NGS.
cfDNA extraction
The QIAseq cfDNA Extraction Kit uses QIAamp Mini Columns to isolate cfDNA from up to 5 ml of plasma. The protocol is specially optimized for NGS with regards to the sensitivity required for variant detection. Following the typical “lyse, bind, wash, elute” steps, cfDNA is first released from histones and selectively bound to the silica membrane. Other contaminants, inhibitors and proteins in the plasma are washed out. In the final step, cfDNA is released from the membrane and eluted in a buffer provided with the kit.
As cfDNA is typically around 170 bp in size, fragmentation prior to library preparation is not required. cfDNA from 1–100 ng in up to 43 µl or 56.5 µl eluant can be directly used for Illumina or Ion Torrent library preparation, respectively.
Library preparation for Illumina sequencers
Library preparation for Illumina sequencers follows a simple one-tube, two-step procedure. In the first step, the ends of the cfDNA are repaired and A-tailed at the 3’ end. This allows the ligation of Illumina-specific sequencing adapters in the second step. The sequencing adapters included with the QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kit are dual-barcoded and are provided in a 96-well sealed plate. This allows multiplexing up to 96 different samples in a single sequencing run. Very limited amounts of cfDNA input of less than 10 ng can be amplified using the high-fidelity PCR master mix included with the kit.
Library preparation for Ion Torrent sequencers
Library preparation for Ion Torrent sequencers uses a proprietary All-in-One reaction that combines end-polishing and adapter ligation. End-repair and adapter ligation are performed in one step in a single tube. QIAseq sequencing adapters provided in the kit are dissolved in duplex buffer and are ready to use. Each well of the 24-plex single-use plate contains equimolar mixes of universal and individual barcode adapters. This allows multiplexing up to 24 different samples in a single sequencing run. Only the adapters supplied with the kit are compatible with the innovative All-in-One end repair and ligation reaction. The kit also contains high-fidelity amplification reagents and primers that are specific for Ion Torrent sequencers to enrich for correct adapter-ligated cfDNA molecules.
Applications
The QIAseq cfDNA All-in-One Kit can be used for any NGS-based cfDNA application. It generates NGS libraries from plasma for any whole genome or hybrid capture sequencing application and is thus suitable for biomarker discovery research, cancer therapy monitoring or non-invasive prenatal testing.
Supporting data and figures
Designed for any NGS-based cfDNA research.