QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit
BAC, PAC, P1 DNA는 최대 50μg까지, 코스미드 DNA는 최대 200μg까지 유전체 DNA가 포함되지 않은 상태로 정제
BAC, PAC, P1 DNA는 최대 50μg까지, 코스미드 DNA는 최대 200μg까지 유전체 DNA가 포함되지 않은 상태로 정제
✓ 연중무휴 하루 24시간 자동 온라인 주문 처리
✓ 풍부한 지식과 전문성을 갖춘 제품 및 기술 지원
✓ 신속하고 안정적인 (재)주문
QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit는 대분자량 DNA의 정제를 위해 중력 흐름(gravity flow) 방식의 음이온 교환 컬럼을 제공합니다. 독자적으로 통합된 ATP 의존적 엑소뉴클레아제 처리 단계가 오염된 유전체 DNA를 선택적으로 제거해 줍니다. 정제된 DNA는 2회 CsCl 구배 원심분리로 얻은 DNA와 동등하며, 트랜스펙션에 적합합니다.
QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit를 이용한 DNA 정제는 최적화된 중력 흐름(gravity flow) 절차를 사용하며, 이 방법을 통해 얻은 DNA는 일반적으로 사용되는 다른 방법들보다 훨씬 더 높은 순도를 자랑합니다. ATP 의존적 엑소뉴클레아제를 이용한 독자적인 통합 처리로 유전체 DNA를 효과적으로 제거할 수 있습니다.
QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit에 포함된 QIAGEN-tips의 독자적인 음이온 교환 수지는 핵산 정제를 위해 특별히 개발되었습니다. 탁월한 분리 특성 덕분에 이 방법으로 얻은 DNA의 순도는 두 번 연속 CsCl 구배 원심분리로 얻은 것과 같거나 이보다 더 우수합니다. 미리 채워진 QIAGEN-tips(그림 ‘ 음이온 교환 팁’ 참고)는 중력의 힘으로 작동하며 건조해지지 않아 플라스미드 준비에 필요한 수작업 시간이 최소화됩니다. QIAGEN의 전체 플라스미드 정제 시스템은 페놀, 클로로포름, 브롬화 에티듐(ethidium bromide), CsCl과 같은 유해 물질을 사용하지 않아 실험자와 환경에 미치는 위험을 최소화했습니다.
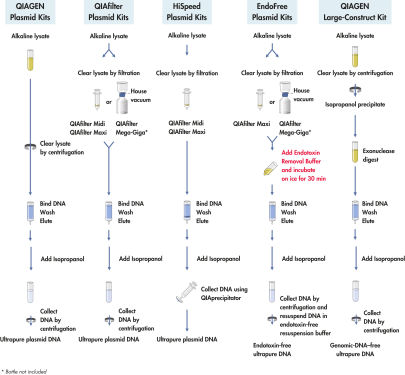
최대 500mL의 배양액을 알칼리 용해한 후(순서도 ‘ QIAGEN 플라스미드 키트 절차’ 참고), 키트에 포함된 ATP 의존적 엑소뉴클레아제를 사용한 독자적인 통합 절단 단계를 적용하여 오염된 유전체 DNA와 절단되거나 손상된 construct DNA를 선택적으로 제거합니다. 그런 다음 샘플을 음이온 교환 팁에 로드하여 적절한 저염 및 pH 조건에서 플라스미드 DNA가 선택적으로 결합되도록 합니다. RNA, 단백질, 대사산물, 기타 저분자량 불순물은 중간 농도의 염 용액으로 세척되어 제거됩니다. 유전체 DNA가 없는 순수한 플라스미드 DNA가 고농도 염 완충액에서 용출됩니다. DNA는 아이소프로판올 침전법으로 농축 및 탈염되고, 원심분리로 회수됩니다.
QIAGEN Large-Construct Kit로 정제된 DNA는 다음을 포함한 모든 응용 분야에 적합합니다.
| 특징 | 사양 |
|---|---|
| Plasmid type | BAC, PAC, P1, 코스미드 DNA |
| Applications | 서브클로닝, 트랜스펙션, 염기서열 분석 등 |
| Processing | 수동(원심분리) |
| Culture volume/starting material | 배양액 부피 <500mL |
| Samples per run (throughput) | 실험당 샘플 1개 |
| Technology | 음이온 교환 기술 |
| Time per run or prep per run | 280분 |
| Yield | <150ug |