Configure at GeneGlobe
Find or custom design the right target-specific assays and panels to research your biological targets of interest.
Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays
Cat. No. / ID: 330261
Array plate and master mix for detection of microbial species or genes
Configure at GeneGlobe To see pricing
Microbial DNA qPCR Arraysは分子生物学的アプリケーション用であり、疾病の診断、予防、あるいは治療に使用することはできません。
Configure at GeneGlobe
Find or custom design the right target-specific assays and panels to research your biological targets of interest.
Features
- 微生物種、毒性因子の遺伝子、または抗生物質耐性遺伝子の同定
- さまざまなサンプルに対応する操作手順
- コントロールアッセイを含むことにより信頼できる結果
Product Details
Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays は、様々なサンプルから関連した微生物種、病原性因子の遺伝子、または抗生物質耐性遺伝子の同定およびプロファイリングするためのアレイです。Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays は、様々なサンプルから関連した微生物種、病原性因子の遺伝子、または抗生物質耐性遺伝子の同定およびプロファイリングするためのアッセイパネルです。種の同定用アッセイは、バクテリアの16S rRNA遺伝子および真菌のrRNA遺伝子をターゲットとし、各アレイには、ホストDNA、バクテリアDNAの含有、PCR反応を確認するためのコントロールが含まれています。また、このキットには、Microbial qPCR Mastermixが含まれています。本アレイの簡便な操作手順は、リアルタイムPCRを使用するいかなる実験室においても、ルーチンで信頼できる微生物遺伝子の同定またはプロファイリングを可能にします。
Performance
直線性のあるダイナミックレンジ
10~106 コピーのDNAテンプレートと、Microbial DNA qPCR Assaysを用いた増幅の結果は直線性を示しました(図 Microbial DNA qPCR Assaysの感度と直線性)。定量下限(Lower limit of quantification;LLOQ)
LLOQとは標準曲線の直線状にのる下限濃度です(図 検出限界と定量下限)。全てのMicrobial DNA qPCR Assaysのうち、93%が100コピー以下のLLOQを示しました(図 高感度であることを示す全Microbial DNA qPCR AssaysのLLOQ)。微生物同定用のアッセイでは92%、毒性因子遺伝子のアッセイは95%、抗生物質耐性遺伝子のアッセイの97%が100コピー以下の定量下限を示しました(図 高感度であることを示す微生物同定用Microbial DNA qPCR AssaysのLLOQ、 高感度であることを示す毒性因子遺伝子検出用Microbial DNA qPCR AssaysのLLOQ、および 高い感度を示す抗生物質耐性遺伝子検出用Microbial DNA qPCR AssaysのLLOQ )。特異性
それぞれのMicrobial DNA qPCR Assayはターゲットとなる種および遺伝子を一つだけ検出するように厳密に検証されています(図 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays の高い特異性)。その他のターゲットも検出するアッセイについては、in silicoで予測された検出対象ターゲットがspecifications sheetに記載されています。この特異性は、糞便、唾液および歯垢のような複雑な生物種を持つサンプルにおいても維持され(図 複雑なメタゲノム使用中の定量にも有効な高感度Microbial DNA qPCR Assays)、様々なシークエンス法でも検証されています(図 パイロシークエンシングによるAntibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array特異性の検証)。
再現性
Microbial DNA qPCR Assaysは同一個体内比較および個体間比較を検証しており、どちらも高い再現性を示します (図 Microbial DNA qPCR Arraysによる信頼できる高い再現性)。See figures
Linearity and sensitivity of Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays.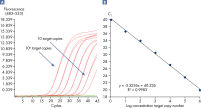 Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification.
Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification.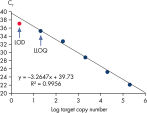 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.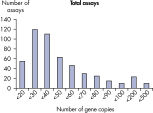 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.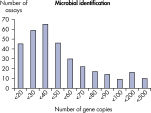 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.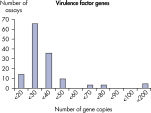 The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.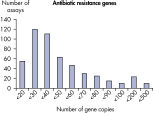 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific.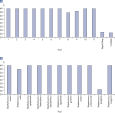 Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.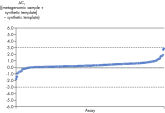 Specificity of the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array is verified by pyrosequencing.
Specificity of the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array is verified by pyrosequencing. Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays generate reliably reproducible results.
Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays generate reliably reproducible results.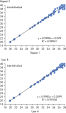
 Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification.
Limit of detection versus lower limit of quantification. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for all Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for microbial identification Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for virulence factor gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity.
The lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) for antibiotic resistance gene detection Microbial DNA qPCR Assays reveals high sensitivity. Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays are highly specific. Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples.
Microbial DNA qPCR Assays display high sensitivity even in complex metagenomic samples. Specificity of the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array is verified by pyrosequencing.
Specificity of the Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Array is verified by pyrosequencing. Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays generate reliably reproducible results.
Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays generate reliably reproducible results.
Principle
Microbial DNA qPCR Assaysは種を同定するために、バクテリアの16S rRNA遺伝子、真菌のrRNA遺伝子配列、病原性因子の遺伝子および抗生物質耐性遺伝子をプライマーおよび加水分解プローブを用いたPCR増幅で検出するようにデザインされています。
Microbial DNA qPCR Arraysは96または384ウェルプレートで関連性の高いアッセイ(例:呼吸器感染に関連する微生物種や、生物防御研究に関する病原体など)で構成されています。各プレートには、確実な結果を得るため、真菌、バクテリアおよび宿主ゲノムDNAの存在コントロール、PCR反応の確認コントロールが含まれております。
Microbial DNA qPCR Arraysは96または384ウェルプレートで関連性の高いアッセイ(例:呼吸器感染に関連する微生物種や、生物防御研究に関する病原体など)で構成されています。各プレートには、確実な結果を得るため、真菌、バクテリアおよび宿主ゲノムDNAの存在コントロール、PCR反応の確認コントロールが含まれております。
Procedure
Microbial DNA qPCR Arrayの操作は簡便で、さらに一般のラボにあるリアルタイムPCR装置にそのまま使用できます。DNAはサンプル種に適応するQIAampキットを用いて抽出し、適切なMicrobial qPCR Mastermixと混合します。反応ミックスをアレイプレートに分注し、リアルタイムPCRによりそれぞれのアッセイから生のCT値が得られます。サンプル中の微生物種または遺伝子の同定およびプロファイリングを行なうことが出来ます。
Applications
Microbial DNA qPCR Arraysは様々なサンプル中の微生物種または遺伝子の同定およびプロファイリングに最適です。たとえば、Vaginal Flora Microbial DNA qPCR Arrayは、細菌性膣炎の基本的な原因の解明に使用でき(図 Vaginal Flora Microbial DNA qPCR Arrayによる頸部スワブサンプルの正確なプロファイリングおよび Gardnerella vaginalis陽性時では正常時と比較して、共生微生物と細菌性膣炎に関連する微生物種が変化)、Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial DNA qPCR Arrayは、腸内または汚泥サンプル中のこれらの遺伝子の同定に有効です(図 Microbial DNA qPCR Arrayによる抗生物質耐性遺伝子が存在する腸内微生物叢のスクリーニングおよび Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial qPCR Arrayによる下水サンプル中抗生物質耐性遺伝子の同定)。
See figures
The Vaginal Flora Microbial DNA qPCR Array provides accurate profiling for cervical swab samples. Vaginal samples positive for Gardnerella vaginalis also show changes in commensal and bacterial vaginosis-related microbes compared to healthy samples.
Vaginal samples positive for Gardnerella vaginalis also show changes in commensal and bacterial vaginosis-related microbes compared to healthy samples.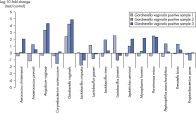 The Microbial DNA qPCR Array screens gut microbiota for the presence of antibiotic resistance genes.
The Microbial DNA qPCR Array screens gut microbiota for the presence of antibiotic resistance genes. The Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial qPCR Array identified antibiotic resistance genes in sewage samples.
The Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial qPCR Array identified antibiotic resistance genes in sewage samples.
 Vaginal samples positive for Gardnerella vaginalis also show changes in commensal and bacterial vaginosis-related microbes compared to healthy samples.
Vaginal samples positive for Gardnerella vaginalis also show changes in commensal and bacterial vaginosis-related microbes compared to healthy samples. The Microbial DNA qPCR Array screens gut microbiota for the presence of antibiotic resistance genes.
The Microbial DNA qPCR Array screens gut microbiota for the presence of antibiotic resistance genes. The Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial qPCR Array identified antibiotic resistance genes in sewage samples.
The Antibiotic Resistance Genes Microbial qPCR Array identified antibiotic resistance genes in sewage samples.
Supporting data and figures
Linearity and sensitivity of Microbial DNA qPCR Arrays.
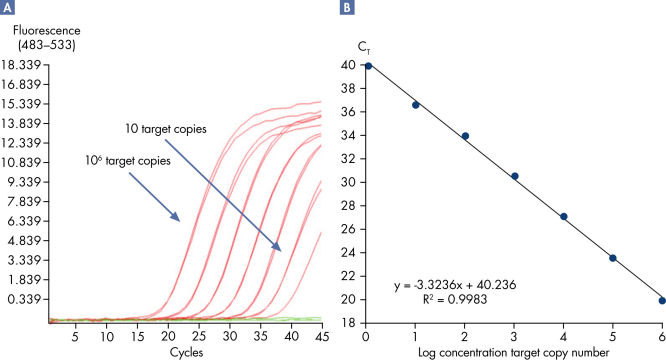
Linearity and sensitivity for each Microbial DNA qPCR Array was determined using synthetic templates over a 6 log serial dilution ranging from 1 copy to 1 million copies. The following are representative results for all the qPCR assays. [A] shows the real-time amplification curves of the KPC antibiotic resistance gene qPCR assay. In [B], a standard curve was prepared that shows that the primer efficiency equals 103% (calculated from slope = –3.3236) and the correlation coefficient is 0.9983, indicating optimum performance for the KPC qPCR assay. All Microbial DNA qPCR Assays have primer efficiencies between 80–120% and correlation coefficients (R)>0.995.
Resources
ダウンロードファイル (20)
MSDS (1)
Supplementary Protocols (4)
ウェビナー (1)
解析用ソフトウェア (1)
パンフレット (2)
サイエンティフィック・ポスター (1)
テクニカルインフォメーション (2)
キットハンドブック (1)
Safety Data Sheets (1)
Certificates of Analysis (1)
Brochures & Guides (2)
Download Files (20)
Analysis Software (1)
Kit Handbooks (1)
Webinars (1)
Scientific Posters (1)
Technical Information (2)
FAQ
What species are detected by the Pan Bacteria 1 and Pan Bacteria 3 Assays?
What sequences are used to design the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What are the storage conditions for the Microbial DNA qPCR products?
What is the difference between LLOQ and LOD?
What is the difference between Positive PCR Control (PPC) and Microbial DNA Positive Control?
Is the Microbial qPCR mastermix used in the Microbial DNA assay and in the Microbial DNA arrays free of genomic bacterial DNA?
What sample types can be tested on the arrays/assays?
Can I measure antibiotic resistance gene expression?
What is the expected amplicon size of the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What is LLOQ?
Can I measure virulence factor gene expression?
Can I use the Microbial DNA-Free Water and Microbial qPCR Mastermix if they have been opened more than 3 times?
How can I calculate the number of bacterial cells that are present in a sample using the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
Are the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays wet-lab verified?
Are the assays species-specific?
Which Microbial qPCR Mastermix should I use?
What are the minimum sample requirements for Microbial DNA qPCR kits?
Which probe labels are available for the Microbial DNA qPCR Assays?
What is the sensitivity for the Microbial DNA qPCR kits?

