✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 31314
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- カラム当たり最大300 μgのHisタグ付加タンパク質をわずか15分ほどで処理
- 非変性条件下や変性条件下での精製
- ワンステップで最大95%の均一性
- 高速自動プロセッシングまたは手動プロセッシングのためのすぐ使用できるスピンカラム
Product Details
Ni-NTAシリカは、Ni-NTAを、非特異的な疎水性相互作用を抑制するために最適化されたマクロ多孔性のシリカ支持材料と組み合わせています。Ni-NTA Spin Kit内のNi-NTA Spin Columns(Hisタンパク質精製用スピンカラム)と別途入手できるNi-NTAシリカは便利なマイクロスピン形式で複数のサンプルを平行して容易に調製することが可能です。それらは、遺伝子工学的に製造されたタンパク質の機能的なスクリーニング、全長翻訳産物を発現するクローンの選択、発現レベルの比較のための簡単な方法を提供します。各スピンカラムは、最大300 µgまでのHisタグタンパク質を精製可能です。すべてのNi-NTAマトリックスと同様に、Ni-NTAスピンカラムは、自然な条件または変性条件下でのワンステップのタンパク質精製のために使用できます。Ni-NTA Spin Kitは、Hisタグタンパク質のスピン精製のための完全なキットで、QIAcube Connect 上で自動化することができます(画像「 QIAcube Connect」を参照)。
See figures
Performance
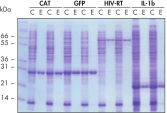
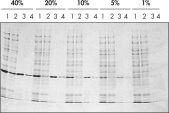
Ni-NTA Spin Columns(His-タンパク質精製用スピンカラム)はまた、Ni-NTA Spin Kitにも同梱されており、再現性の高い高速自動精製を(図 “再現性の高い自動精製”を参照)様々な異なる発現レベルで可能です(図 “異なる発現レベルでの精製”を参照)。
See figures
Principle
Ni-NTA Spin ColumnとNi-NTA Spin Kitを含むQIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification Systemは、6個以上のヒスチジン残基のアフィニティータグ – Hisタグを含むタンパク質に対する特許取得済みのNi-NTA(ニッケル-ニトリロ三酢酸)樹脂の顕著な選択性に基づいています。この技術により、非変性条件下または変性条件下でいかなる発現系からでもほぼあらゆるHisタグ付加タンパク質をワンステップで精製することが可能です。NTAはニッケルイオンに対して4つのキレーション部位を持っているため、金属イオンとの相互作用に利用できる3つの部位だけを持つ金属キレート精製システムよりもニッケルを強く結合します。余分なキレーション部位はニッケルイオンの浸出を防ぎ、その結果、より大きな結合能力を持つことができ、他の金属キレート精製システムを使用したものよりも高純度でタンパク質を精製することができます。QIAexpressシステムを使用して、バキュロウイルス、哺乳類細胞、酵母、細菌などのあらゆる発現系からHisタグタンパク質を精製できます。
Procedure
Hisタグタンパク質の精製は、4段階で構成されています:細胞溶解、結合、洗浄、溶出(図 “Ni-NTAタンパク質精製システムでのNi-NTA Spin Column精製”を参照)。QIAexpressシステムを使用した遺伝子組み換えタンパク質の精製は、タンパク質やHisタグの3次元構造に依存しません。これにより、希釈溶液や粗溶解物からの、自然条件または変性条件下でのワンステップのタンパク質精製が可能になります。最大600 μlの細胞溶解物をNi-NTAスピンカラム上に充填できます。2分間のスピンでタグタンパク質はNi-NTAシリカに結合し、その一方で大部分のタグのないタンパク質は流れ出ます。洗浄段階の後、精製されたタンパク質は、温和な条件下(pH 5.9まで低下、または100~500 mMイミダゾールの添加など)で、100-300 μlの体積内に溶出します。Hisタグは小さく、ほぼ免疫性がないため、Hisタグの除去は通常は不要です。精製されたタンパク質は、すぐに使用できます。タンパク質は、複数の小規模な発現培地からはおよそ30分(手動)、またはおよそ60分(QIAcube Connectでの自動化)で精製することができます。強い変性剤や洗浄剤を使用して、レセプター、膜タンパク質、および封入体を形成するタンパク質を効率的に可溶化し精製できます。非特異的に結合する混入物の効率的な除去を可能にする試薬は、洗浄バッファーに含めることができます(表を参照)。精製されたタンパク質は、100~250 mMイミダゾールを競合剤として添加するか、pHを下げることにより温和な条件下で溶出します。
Ni-NTA–His相互作用に適合する試薬
- 6 M グアニジン塩酸塩
- 8 M 尿素
- 2% Triton X-100
- 2% Tween 20
- 1% CHAPS
- 20 mM β-ME
- 10 mM DTT
- 50% グリセロール
- 20% エタノール
- 2 M NaCl
- 4 M MgCl2
- 5 mM CaCl2
- ≤20 mM イミダゾール
- 20 mM TCEP
See figures
Applications
Ni-NTA Spin ColumnとNi-NTA Spin Kitを含むQIAexpress Ni-NTA Protein Purification Systemは、以下をはじめとするあらゆるアプリケーションに適した信頼性の高いワンステップのタンパク質精製を実現します。
- 構造的および機能的調査
- 3次元構造決定のための結晶化
- タンパク質–タンパク質およびタンパク質–DNA相互作用を含むアッセイ
- 抗体を産生するための免疫付与
| 機能 | Ni-NTA Spin Column | Ni-NTA Spin Kit |
| アプリケーション | プロテオミクス | プロテオミクス |
| ビーズのサイズ | 16–24 µm | 16–24 µm |
| 結合能 | スピンカラム当たり最大300 µg | スピンカラム当たり最大300 µg |
| 重力流またはスピンカラム | スピンカラム | スピンカラム |
| プロセッシング | 自動化/手動 | 自動化 |
| 規模 | 小規模 | 小規模 |
| 特殊機能 | ロースループットスクリーニング | ワンステップで最大95%の均一性 |
| 出発材料 | 細胞溶解物 | 細胞溶解物 |
| 支持体/マトリックス | マクロ多孔性シリカ | マクロ多孔性シリカ |
| タグ | 6xHisタグ | 6xHisタグ |
Supporting data and figures
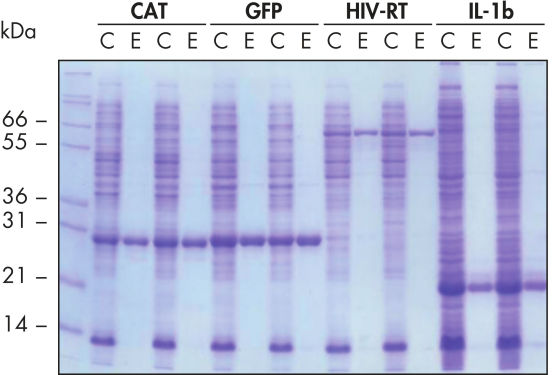
再現性の高い自動化精製。
示したタンパク質は、手動またはQIAcube上での自動化手順で、 5 ml LB培地由来のクリアなE. coli溶解物から、Ni-NTA Spin Columnを使用して非変性条件下で二重に精製した。CAT:クロラムフェ二コールアセチルトランスフェラーゼ、GFP:緑色蛍光タンパク質、HIV-RT:ヒト免疫不全ウイルス逆転写酵素、IL-1b:インターロイキン-1β。M:マーカー、C:クリアライセート(1レーン当たり2 μlを充填)、E:溶出分画(1レーン当たり3 μlを充填)。