✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 79306
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- 遺伝子発現解析に使用するRNA精製に至適化された溶解条件
- 脂肪の多い組織から高収量のRNA
- 溶解とホモジナイゼーションのための解りやすいプロトコール
- フェノールのキャリーオーバーを回避するためのRNeasyクリーンアップを統合
- 様々な組織タイプに対応
Product Details
QIAzol Lysis Reagent は、脂質を多く含む組織の溶解に最適です。QIAzol標準プロトコールは、簡単な操作手順で、QIAzol による溶解と一般的なホモジナイゼーション法、エタノール沈殿を組み合わせます。
Performance
See figures
Principle
フェノール・グアニジンをベースにしたQIAzol Lysis Reagent は、あらゆる種類の組織の溶解に使用することができますが、脳組織、脂肪組織などの脂質に富んだ組織の溶解に至適化されています。有機溶媒抽出とカオトロピック塩による破砕とを組み合わせることで、組織を効率的に溶解し、トータルRNAを高い収量で得ることができます。有機溶媒抽出ステップではタンパク質とDNAの双方が除去されることで、沈殿およびスピンカラムなどの精製ステップの効率が高まります。QIAGENでは、QIAzol による溶解とRNeasyシリカメンブレン精製テクノロジーを統合し、ひとつの簡単なプロトコールにおいて統合された効率的なRNA精製ソリューションも提供しています(あらゆる種類の組織を対象としたRNeasy Plus Universal Kitsなど)。
Procedure
QIAzol標準プロトコールはQIAzol による溶解と一般的なホモジナイゼーション法、エタノール沈殿を組み合わせた解りやすい操作手順です。組織サンプルをQIAzol Lysis Reagent中でホモジナイズし、クロロホルムを添加した後、ホモジネートを遠心操作により、水層と有機溶媒層に分離します。DNAは中間層、タンパク質は下の有機溶媒層に、そしてRNAは上の水層に分画されます。イソプロパノールを添加してRNAを水層から沈殿させ、その後にエタノールで洗浄したペレットをRNaseフリーの水で溶解します。ダウンストリームアプリケーションで良好な実験結果を得るためには、その後、混入しているフェノールを取り除き、RNAを濃縮するためにRNeasy MinElute Cleanup Kitを用いてRNAを精製することをお薦めします。
Applications
フェノール・グアニジンをベースにしたQIAzol Lysis Reagent は、脳や脂肪組織のような脂質を多く含む組織の溶解に最適です。ダウンストリームアプリケーションで最高の実験結果を得るためには、RNeasy Plus Universal KitあるいはRNeasy MinElute Cleanup Kitを用いてRNAを精製することをお薦めします。
Supporting data and figures
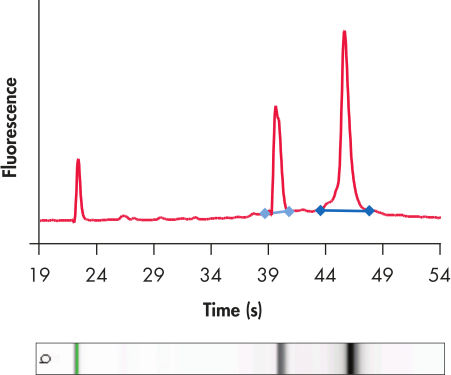
High-quality RNA.
Total RNA was isolated from 200 mg rat adipose tissue using the RNeasy Lipid Tissue Midi Kit (with QIAzol). The high quality of the RNA is shown by scanning with the Agilent 2100 BioAnalyzer.