QIAfilter Plasmid Kits
10 mgまでのトランスフェクショングレードのプラスミドあるいはコスミドDNAの迅速な精製用
10 mgまでのトランスフェクショングレードのプラスミドあるいはコスミドDNAの迅速な精製用
✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
Cat. No. / ID: 12243
✓ オンライン注文による24時間年中無休の自動処理システム
✓ 知識豊富で専門的な製品&テクニカルサポート
✓ 迅速で信頼性の高い(再)注文
QIAfilter Plasmid Kitsは、ろ過によるバクテリアライセートの清澄化を含んだ陰イオン交換ベースのプラスミド精製を実現します。精製したDNAは、CsCl密度勾配遠心操作を2回行なって得られる精製グレードに匹敵し、トランスフェクション等のアプリケーションに最適です。
QIAfilter Plasmid Kitsは、遠心操作の代わりにバクテリアライセートの清澄化をろ過操作で迅速に行なうQIAfilter Cartridgesと、効率的なプラスミド精製法として実績のある陰イオン交換樹脂が充填されたQIAGEN-tip を組み合わせたキットです。それぞれ、10 mg(Giga)、2.5 mg(Mega)、500 µg(Maxi)、100 µg(Midi)までのトランスフェクショングレードの高コピー数プラスミドDNAを培養液から精製します(培養液の容量はプラスミドコピー数、挿入サイズ、宿主株、培養液に依存します)。
低コピー数のプラスミド、コスミドの精製では、必要な培養液の容量が大きく、QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridgesの容量が限られているため、QIAfilter Plasmid Giga KitよりQIAfilter Plasmid Mega Kitの使用をお薦めします。
QIAfilter、HiSpeedおよびEndoFree Plasmid Kitsに添付されているQIAfilter Cartridgesは、バクテリア細胞のアルカリ溶解後に行なう遠心操作による清澄化に代わる方法としてデザインされた特別なフィルターです。QIAfilter CartridgesはSDS沈殿物を完全に取り除くばかりではなく、遠心操作に必要な時間よりも迅速にバクテリアライセートの清澄化が可能なので、プラスミド精製時間を最大1時間短縮できます。
QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridgesでは、大量のバクテリアライセートでも簡単かつ効率的に清澄化できるように吸引法を利用しています。QIAfilter Mega および Midi Cartridgesは、シリンジフォーマットで、液体を注入することにより溶解物がフィルターを通過し、すばやく清澄化されます。
QIAGEN-tip中のユニークな陰イオン交換樹脂は核酸精製のみを目的として開発されました。本製品の優れた核酸分離能力により、CsCl密度勾配遠心操作を2回連続で行なって得たDNAの純度に匹敵、あるいはそれ以上の純度のDNAが調製されます。充填済みQIAGEN-tipsはオープンカラムで操作し、乾燥することはなく、プラスミド調製に必要なマニュアルでの作業時間を短縮できます。全てのQIAGENプラスミド精製システムでは、ユーザーおよび環境への影響が最小限となるように、フェノール、クロロホルム、臭化エチジウム、CsCl等の有害な試薬を一切使用していません。
特徴 | QIAfilter Plasmid Giga Kit | QIAfilter Plasmid Mega Kit | QIAfilter Plasmid Maxi Kit | QIAfilter Plasmid Midi Kit |
| Applications | Transfection, cloning, sequencing, etc. | Transfection, cloning, sequencing, etc. | Transfection, cloning, sequencing, etc. | Transfection, cloning, sequencing, etc. |
| Culture volume/starting material | 2.5 liters culture volume | 500 ml – 2.5 liters culture volume | 100–250 ml culture volume | 25–50 ml culture volume |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Processing | Manual (filtration) | Manual (filtration) | Manual (filtration) | Manual (filtration) |
| Sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run |
| Technology | Anion-exchange technology | Anion-exchange technology | Anion-exchange technology | Anion-exchange technology |
| Time per run | 280 min | 190 min | 120 min | 110 min |
| Yield | <10 mg | <2.5 mg | <500 µg | <100 µg |
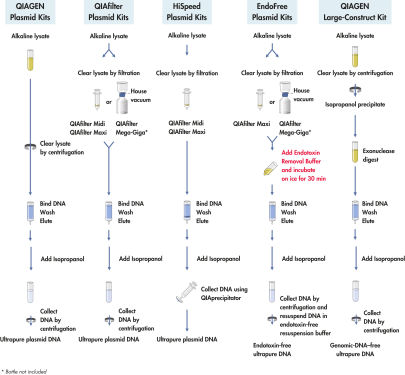
中和したバクテリアライセートをQIAfilter Cartridges中で直接インキュベートし、ろ過により迅速に清澄化します。清澄化されたライセートを陰イオン交換チップ上にロードすると、適切な低塩あるいはpH条件でプラスミドDNAが選択的に結合します。RNA、タンパク質、代謝物、その他の低分子量不純物は中濃度の塩による洗浄で取り除かれ、超高純度プラスミドDNAが高塩濃度のバッファーで溶出されます(フローチャート" QIAGEN Plasmid Kits操作手順")。イソプロパノール沈殿によりDNAが濃縮および脱塩され、遠心操作により回収されます。
QIAfilter Plasmid Kitsで精製されたDNAは、クローニングからトランスフェクションまでの幅広いアプリケーションに最適です。