N-Terminus pQE Vector Set
N末端Hisタグ付加タンパク質を高レベルで発現させるために
N末端Hisタグ付加タンパク質を高レベルで発現させるために
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 32915
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
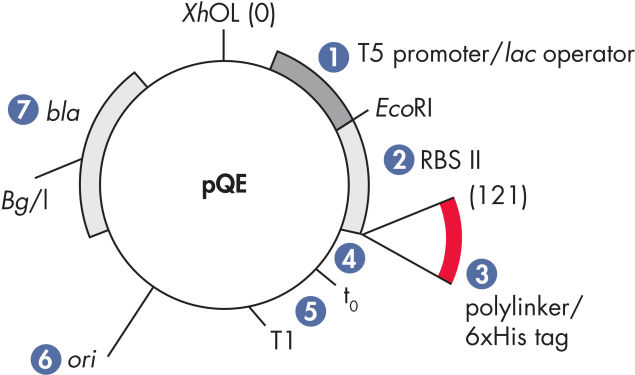
このセットは、N末端にHisタグのあるタンパク質の発現用に、5つのベクター(pQE-9、pQE-30、pQE-31、pQE-32、pQE-40)を提供します。pQE-30、pQE-31、pQE-32は、3つのリーディングフレームすべてにマルチプルクローニングサイト(MCS)を提供しますが、pQE-9は、代わりにより短いマルチプルクローニングサイトを持っています。pQE-40は、DHFR融合タンパク質の発現向けに設計されており、発現レベルの低いタンパク質または短いペプチドの発現用にお勧めします。それらは、タンパク質分解されやすいのですが、それはDHFRが安定性と抗原性を高めることによります。DHFR自体は、マウスやラットではほとんど免疫性がないため、DHFR融合タンパク質はエピトープのスクリーニングに最適です。
| 要素 | 説明 |
| 最適化されたプロモーター/オペレーターエレメント | ファージT5プロモーターと2つのlacオペレーター配列で構成され、それによりlacリプレッサー結合の可能性が上がり、強力なT5プロモーターの効率的な抑制を保証します |
| 合成リボソーム結合部位RBSII | 効率的な翻訳のために |
| 6xHisタグコード配列 | ポリリンカークローニング領域への5’または3’のいずれか |
| 翻訳終止コドン | 発現コンストラクトの便利な調製のため、すべてのリーディングフレーム内 |
| 2つの強力な転写ターミネーター | 読み過ごし転写を防ぎ、発現コンストラクトの安定性を保証するため、ファージλ由来のt0、およびE. coliのrrnBオペロン由来のT1 |
| ColE1複製開始点 | pBR322由来 |
| βラクタマーゼ遺伝子(bla) | アンピシリン耐性を与えます |
目的のタンパク質をコードするインサートは、適切なコンストラクト内にクローニングされ(詳しくは、QIAexpressionist ハンドブックを参照)、発現のために適切なE. coli株内に転換されます。発現は、IPTGの添加によって誘導されます。Vector pQE-TriSystemのコンストラクトは、E.coli内に転換されたり、昆虫細胞内での遺伝子組み換えタンパク質の発現のためにシャトルベクターとして使用されたり、哺乳類細胞内に導入されたりします。
QIAexpress Expressionシステムは、以下をはじめとする
数多くのアプリケーションに適したタンパク質の高レベル発現を実現します。
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Expression | In vivo |
| Tag | 6xHisタグ |
| N- or C-terminal tag | N末端タグ |
| Expression species | 大腸菌 |
| Tag removal sequence | いいえ |
| In-frame cloning necessary | はい |
| All three reading frames provided | はい |