✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 180450
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Stranded, high-quality RNA-seq libraries for transcriptome analysis
- Only 100–5000 ng of total RNA or 1–100 ng of poly-A+ enriched RNA required
- Includes QIAseq Beads and sample adapter plates
- Compatible with fresh, as well as FFPE samples
- Includes access to the RNA-seq Analysis Portal for human, mouse and rat samples
Product Details
QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits provide a superior method for generating Illumina compatible RNA-seq libraries from total RNA or mRNA enriched samples. For applications such as gene expression, fusion gene or mutation detection, QIAseq Stranded mRNA Select Kits include an optimized mRNA enrichment protocol with all the reagents and components required to build high-quality RNA-seq libraries. QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits use a unique protocol, which does not require actinomycin D to retain strand specificity or dUTP to ensure stranded library construction, thereby ensuring highly sensitive detection of low-expression RNA molecules with increased complexity and transcript coverage. QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits use CleanStart HiFi PCR Mastermix to ensure high-fidelity amplification of libraries and to protect from PCR contamination. CleanStart HiFi PCR Mastermix is included in each kit or can be used separately with other library preparation methods.
Analyze stranded RNA-seq data with ease using the GeneGlobe-integrated RNA-seq Analysis Portal – an intuitive, web-based data analysis solution created for biologists and included with QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits.
Want to try this solution for the first time? Request a quote for a trial kit.
For one-step, rRNA and globin mRNA removal in just 20 minutes, use QIAseq FastSelect –rRNA HMR Kits.
Performance
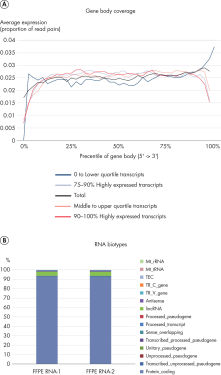
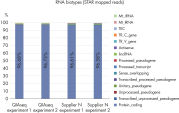
QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits provide a superior method for generating high-quality RNA-seq libraries compatible with Illumina sequencers in just 4–5 hours (see figures " Preparation of Stranded RNA-seq Libraries in 1 Day" and " Reproducible Transcript Profiles with Different RNA Input Amounts"). Compared to kits from alternative suppliers, QIAseq Kits ensure high library complexity with low duplication rates, as well as high yields of libaries (see figure " High Library Complexity and Low Duplication Rates"). When using the highly optimized QIAseq mRNA enrichment protocol, more than 96% of the reads are mapped to protein coding regions, which is indicative of the high efficiency and specificity of the QIAseq mRNA enrichment and library construction steps (see figure " RNA Biotype Distribution: High Efficiency of mRNA Enrichment Protocol"). High-quality RNA-seq data is generated, even from highly degraded FFPE samples (see figure " RNA-seq Data from Highly Degraded RNA").
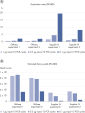
High mapping quality with different data analysis pipelines
QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits ensure high rates of uniquely mapped reads, allowing you to optimize the amount of reads you can use for your downstream NGS data analysis and help to save time and costs (see tables below).
| QIAseq experiment 1 | QIAseq experiment 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Reads mapped in pairs | 91.86% | 92.28% |
| Reads mapped in broken pairs | 4.84% | 4.47% |
| Reads not mapped | 3.29% | 3.25% |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
| QIAseq experiment 1 | QIAseq experiment 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Uniquely mapped reads | 92.02% | 91.69% |
| Reads mapped to multiple loci | 4.51% | 4.55% |
| Reads mapped to too many loci | 0.05% | 0.05% |
| Reads mapped: Too short | 3.38% | 3.68% |
| Reads mapped: Other | 0.04% | 0.04% |
| Total | 100 | 100 |
Superior Lower limit of Detection (LoD)
QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits show high levels of sensitivity with regards to the detection of low-abundance transcripts. Even minimal amounts of RNA molecules lead to sufficient NGS reads, which ensures accurate transcript identification from low-expression genes.
High library complexity with low duplication rates
Highly optimized enzymology with optimized protocols result in RNA-seq libraries with high complexity and minimal duplication. This ensures that QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits deliver the maximum amount of data from each sample, even when starting with low amounts of RNA.
New CleanStart PCR formulation actively removes contaminants
The CleanStart PCR enrichment step uses a high-fidelity DNA polymerase to ensure accurate amplification of your RNA-seq library, while also providing an integrated method to remove PCR contamination.
See figures
Principle
QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits enable fast, efficient and accurate NGS library construction from not only high-quality mRNA, but also low-quality fragmented total RNA of various origins. After an optional RNA fragmentation step, the reverse transcription step generates first strand cDNA.
Strand specificity is ensured due to optimized combinations of RT enzyme and buffer provided by QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits, removing the need to use toxic reagents such as actinomycin D. In the second strand synthesis step, a special combination of enzymes with carefully adapted buffer formulations allow the degradation of RNA, the generation of a second cDNA strand and the generation of blunt DNA ends and A-base addition necessary for efficient ligation of the Illumina compatible adapters. The special strand-specific ligation step of the QIAseq Stranded RNA Kit protocol ensures strand specificity without the need for additional reagents or laborious and time-consuming protocol steps. The included adapter plates with dual index technology can be used for the sequencing of multiple samples (up to 96). The CleanStart PCR mix efficiently amplifies the generated RNA-seq library irrespective of high GC or AT sequences, and also degenerates contaminating material such as previously generated NGS libraries. The paramagnetic QIAseq Beads included with kits provide fast and efficient reaction cleanup between protocol steps. High-quality RNA-seq libraries can be generated in just 4–5 hours.
Procedure
RNA fragmentation and reverse transcription
The RNA fragmentation step using the reverse transcription buffer ensures the generation of RNA libraries with optimal insert sizes. The fragment size can be adapted by shorter or longer incubation times. The protocol also allows the use of input RNA that has already been fragmented, as well as heavily degraded low-quality FFPE RNA. In the reverse transcription step, optimized RT enzyme and buffer formulations ensure strand specificity during cDNA generation. Toxic reagents such as actinomycin D, which negatively affects reverse transcription efficiency, is not required.
Second strand synthesis / end-repair / A-addition
The enzyme mix and buffer formulation are optimized to complete second strand synthesis, end-repair and A-addition in a very short time. First, RNA molecules are degraded. Next, cDNA molecules are used as templates to generate a second cDNA strand. Then, blunt double-stranded DNA is generated. Finally, an A-nucleotide is added to the 5' end of the cDNA. A modification of dexoynucleotides, which is needed with the dUTP method, is not required and ensures optimal efficiency of cDNA generation.
Illumina compatible adapter ligation
Strand-specific ligation of Illumina compatible adapters enables fast and efficient generation of RNA-seq libraries with cDNA prepared from the previous library preparation step. The strand-origin information of the initial RNA can be maintained without additional reagents, modified nucleotides or protocol steps. The included ready-to-use adapter plates allow the sequencing of up to 96 different samples by the combination of a unique 8-nucleotide i5 and i7 index barcode.
CleanStart PCR enrichment
The QIAGEN proprietary CleanStart PCR Mix efficiently and uniformly amplifies the RNA-seq library regardless of the G/C content of the template, while also protecting against PCR contamination. The combination of an optimized buffer formulation and a Hotstart HiFi polymerase enzyme ensures low mutation rates and high processivity for the enrichment of an RNA-seq library. The CleanStart decontamination step allows the removal of contaminating material, such as previously generated NGS libraries, to maximize sample purity.
Applications
QIAseq Stranded RNA Library Kits generate RNA-seq libraries from low RNA amounts of various origins and species. The resulting highly complex and strand-specific NGS libraries, in combination with the decontaminating properties of the CleanStart PCR Mix, allow the analysis of even low-abundance transcripts with high sensitivity. The streamlined, 4–5 hour protocol allows the generation of NGS libraries, library QC measurements and the start of an NGS sequencing run in just one working day.
Supporting data and figures
RNA-seq Data from Highly Degraded RNA..