✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 301704
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- Efficient transfection using low siRNA concentrations
- Effective transfection of primary cells with high cell viability
- Effective transfection of suspension cells and macrophages
- Cell-specific protocols at the TransFect Protocol Database
- Efficient transfection of miRNA mimics or inhibitors
Product Details
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent is a unique blend of cationic and neutral lipids that enables effective siRNA uptake and efficient release of siRNA inside cells, resulting in high gene knockdown even when using low siRNA concentrations. In addition to siRNA, HiPerFect Transfection Reagent is ideally suited to transfection of miRNA mimics or inhibitors. Cell-type-specific protocols using HiPerFect Transfection Reagent are available at the TransFect Protocol Database.
Performance
A range of suspension cell lines and differentiated and undifferentiated macrophages have been tested using HiPerFect Reagent for siRNA transfection. Many lines were successfully transfected with excellent knockdown of target gene expression (see Table 1). Transfection with HiPerFect Reagent is a superior alternative to electroporation for many of these cell types.
| Cell line | Cell type | siRNA concentration | Knockdown |
| K562 | Human chronic myeloid leukemia | 5 nM | 85% |
| Jurkat | Human T-cell | 75 nM | 83% |
| D1.1 | Human T-cell | 50 nM | 84% |
| RAW 264.7 | Mouse macrophage | 25 nM | 77% |
| J774.A1 | Mouse macrophage | 50 nM | 97% |
| PMA-differentiated THP-1 | Human acute monocytic leukemia | 5 nM | 82% |
| MEL | Murine erythroleukemia | 5-20 nM | 50-70% |
Some cell lines were not amenable to transfection using HiPerFect Reagent (see Table 2).
| Cell line | Cell type |
| Raji | Human B-cell |
| U937 | Human macrophage |
| Molt4 | Human T-cell |
| Molt14 | Human T-cell |
| HL60 | Promyelocytic cell line |
| E6.1 | Human T-cell |
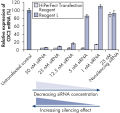
Efficient knockdown (>80%) is achieved with siRNA concentrations in the range of 1–50 nM (see figure " HiPerFect Reagent provides effective CDC2 knockdown"). Transfection of 1 nM siRNA resulted in 86% knockdown and transfection of 5 nM siRNA increased the knockdown efficiency to 96%. Depending on the purpose of the RNAi experiment, the optimal concentration of siRNA to use may be 1 nM (minimal risk of off-target effects and efficient knockdown) or 5 nM (higher knockdown efficiency).
See figures
Principle
Transfection of siRNA can result in off-target effects, in which siRNAs affect the expression of non-homologous or partially homologous gene targets. Off-target effects, which may produce misleading results in RNAi experiments, can be largely avoided by using low siRNA concentrations. Using HiPerFect Transfection Reagent, highly efficient transfection and silencing have been observed, in some cases with as little as 10 pM siRNA. HiPerFect Transfection Reagent provides highly efficient siRNA transfection over a range of siRNA concentrations from low to high, allowing researchers to choose the siRNA concentration they wish to use. It can be used to transfect a wide range of cell types, including HeLa, HeLa S3, HEK 293, NIH/3T3, Huh-7, HepG2, MCF-7, HUVEC, and NHLF (see figure " Efficient transfection of NHEK").
miRNA research
microRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous small RNA molecules with similar characteristics to siRNAs. miRNAs play a role in many diverse biological processes such as development, differentiation, and apoptosis. Transfection of synthetic miRNA mimics or inhibitors is a technique used to elucidate the targets and roles of particular miRNAs. miRNA mimics are chemically synthesized miRNAs which mimic naturally ocurring miRNAs upon transfection into the cell. miRNA inhibitors are single-stranded modified RNAs which specifically inhibit miRNA function. Reduced gene expression after transfection of an miRNA mimic, or increased expression after transfection of an miRNA inhibitor, provide evidence that the targeted miRNA is involved in regulation of that gene. Alternatively, the role of miRNAs in various pathways can be studied by examination of a specific phenotype after transfection of an miRNA mimic or inhibitor. HiPerFect Transfection Reagent was developed for highly efficient transfection of eukaryotic cells with siRNA, and is ideally suited to transfection of miRNA mimics or inhibitors.
See figures
Procedure
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent is provided as a ready-to-use solution - just add the reagent to your diluted siRNA/miRNA, mix, incubate, and pipet the complexes onto the cells. Transfections can be performed in the presence of serum, eliminating the need to remove complexes from the cells. In addition to the protocols provided in the HiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook, you can find protocols to suit your cell type and plate/dish format using the TransFect Protocol Database. The database takes the guesswork out of transfection protocols. Rather than adapting existing protocols to fit your requirements, the database provides exactly the protocol needed, saving time and effort. Simply enter the cell type, nucleic acid, and plate format to receive a QIAGEN transfection protocol to print out or download in convenient PDF format. Use of the TransFect Protocol Database is free of charge and no registration is required.
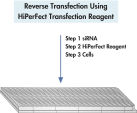
Transfection with HiPerFect Transfection Reagent can be carried out using the common transfection procedure of seeding the cells 24 hours before transfection. Alternatively, protocols are provided for reverse transfection in 96-well plates and 384-well plates (see theHiPerFect Transfection Reagent Handbook). In these protocols, cells are seeded and transfected in the same day. siRNA/miRNA is spotted into wells followed by the addition of HiPerFect Reagent. After complex formation, cells are added to the wells (see flowchart " Reverse transfection using HiPerFect Transfection Reagent"). Reverse transfection protocols are rapid, convenient, and can easily be automated.
See figures
Applications
HiPerFect Transfection Reagent enables highly efficient siRNA transfection, even with low siRNA concentrations, for applications such as:
- RNA interference studies
- miRNA research
- Studies on gene expression and function
Supporting data and figures
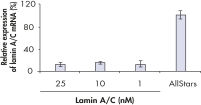
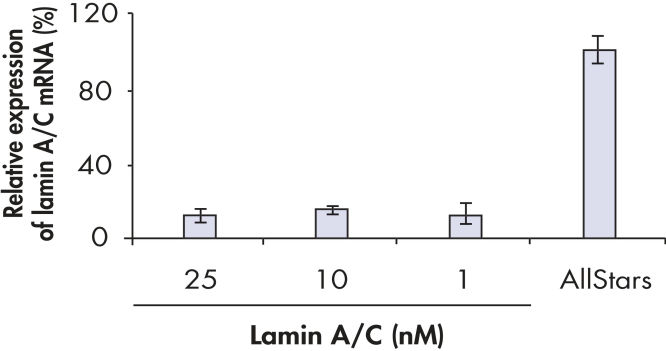
Efficient transfection of NHEK with HiPerFect Reagent.
Normal human embryonal keratinocytes were transfected with siRNA targeting lamin A/C or with AllStars Negative Control siRNA. Lamin A/C expression was measured by real-time RT-PCR after 48 hours.
Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| Applications | RNAi studies, gene expression studies |
| Transfection type | Transient transfection |
| Features | Minimized risk of off-target effects, rapid reverse transfection |
| Nucleic acid | siRNA, miRNA |
| Technology | Cationic and neutral lipids |
| Controls | Not included |
| Cell type | Eukaryotic cells including primary cells |
| Number of possible transfections | 333 transfections in 24-well plates / 1 ml reagent |