✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 33903
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Features
- No need for time-consuming subcloning procedures
- Obtain post-translational modifications in insect or mammalian cells
- One construct provides efficient expression in three expression systems
Product Details
Performance
See figures
Principle
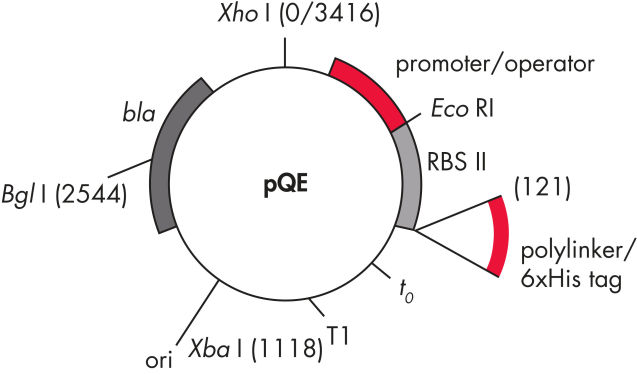
QIAexpress pQE vectors combine a powerful phage T5 promoter (recognized by E. coli RNA polymerase) with a double lac operator repression module to provide tightly regulated, high-level expression of recombinant proteins in E. coli. Protein synthesis is effectively blocked in the presence of high levels of lac repressor and the stability of cytotoxic constructs is enhanced. The pQE vectors (see table and figure pQE Vectors) enable placement of the 6xHis tag at either the N- or C-terminus of the recombinant protein.
| Element | Description |
| 1. Optimized promoter/operator element |
Consists of the phage T5 promoter and two lac operator sequences, which increase the probability of lac repressor binding and ensure efficient repression of the powerful T5 promoter |
| 2. Synthetic ribosomal binding site RBSII | For efficient translation |
| 3. His-tag coding sequence | Either 5' or 3' to the polylinker cloning region |
| 4. Translational stop codons | In all reading frames for convenient preparation of expression constructs |
| 5. Two strong transcriptional terminators |
t0 from phage lambda, and T1 from the rrnB operon of E. coli, to prevent read-through transcription and ensure stability of the expression construct |
|
6. ColE1 origin of replicatio |
From pBR322 |
| 7. beta-lactamase gene (bla) | Confers ampicillin resistance |
See figures
Procedure
Inserts encoding proteins of interest are cloned into appropriate constructs and transformed into a suitable E. coli strain for expression. Expression is induced by addition of IPTG. Vector pQE-TriSystem constructs can be transformed into E. coli, used as a shuttle vector for recombinant protein expression in insect cells, or transfected into mammalian cells.
Applications
The QIAexpress Expression System provides high-level expression of proteins suitable for
many applications, including:
- Purification of functional, conformationally active proteins
- Purification under denaturing conditions for antibody production
- Crystallization for determination of three-dimensional structure
- Assays involving protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions
Supporting data and figures
pQE Vectors.
Numbered elements listed in table.
Specifications
| Features | Specifications |
|---|---|
| In-frame cloning necessary | Yes |
| Expression | In vivo |
| Tag removal sequence | No |
| Expression species | E.coli, mammalian & insect cells |
| Tag | 6xHis tag |
| N- or C-terminal tag | C-terminal tag |
| All three reading frames provided | No |