EndoFree Plasmid Kits
For purification of up to 10 mg endotoxin-free advanced transfection-grade plasmid or cosmid DNA
For purification of up to 10 mg endotoxin-free advanced transfection-grade plasmid or cosmid DNA
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
Cat. No. / ID: 12362
✓ 24/7 automatic processing of online orders
✓ Knowledgeable and professional Product & Technical Support
✓ Fast and reliable (re)-ordering
EndoFree Plasmid Kits provide anion-exchange-based endotoxin-free plasmid DNA purification. QIAfilter Cartridges enable fast lysate clearing by filtration. The purified DNA exceeds the purity obtained by 2 x CsCl gradient centrifugation and is suitable for advanced transfection-grade applications. The EndoFree Plasmid Buffer Set can be used for preparations of 10 mega or 5 giga transfection-grade plasmid or cosmid DNA preparations.
The EndoFree Plasmid Kits integrate an efficient endotoxin removal step into the plasmid purification procedure — no additional extractions or affinity columns to remove lipopolysaccharides are required. Bacterial lysates are cleared by filtration with a QIAfilter Mega-Giga or Maxi Cartridge, and plasmid DNA is purified on gravity-flow QIAGEN-tips containing anion-exchange resin. Yields of up to 500 μg (maxi), 2.5 mg (mega), and 10 mg (giga) purified DNA are achieved from culture (culture volumes depend on plasmid copy number, size of insert, host strain, and culture medium). Purified DNA is endotoxin free (<0.1 EU/µg DNA).
For purification of low-copy plasmids and cosmids, the EndoFree Plasmid Mega Kit is a better choice than the EndoFree Giga Plasmid Kit, due to the large culture volumes required and the limited capacity of the QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridge.
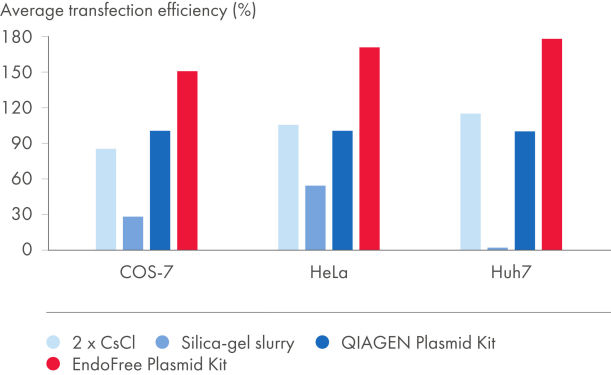
EndoFree Plasmid Kits remove bacterial endotoxins which are released during the lysis step and influence transfection of DNA into primary cells and sensitive cultured cells. The endotoxin-free DNA obtained from the EndoFree Plasmid Kits is highly suited for reproducible and reliable results in transfection (see figures Plasmid purification method versus transfection efficiency and Plasmid purity versus transfection efficiency and tables "Endotoxin levels in plasmid preparations" and "EndoFree DNA yields high transfection efficiencies with primary cells"). QIAGEN ultrapure endotoxin-free DNA is also suitable for gene therapy research and other sensitive applications.
| Plasmid preparation method | Endotoxin (EU†/µg DNA) |
Average transfection efficiency‡ |
| EndoFree Plasmid Kit | 0.1 | 154% |
| QIAGEN Plasmid Kit | 9.3 | 100% |
| 2x CsCl | 2.6 | 99% |
| Silica-gel slurry | 1230.0 | 24% |
| DNA purification method | Percentage of transfected cells |
| EndoFree Plasmid Kit | 21.0% ± 0.93 |
| QIAGEN Plasmid Kit | 8.1% ± 0.57 |
| Silica-gel slurry | 5.2% ± 0.74 |
The level of endotoxin contamination in purified plasmid DNA depends on the purification method used (see table "Endotoxin levels in plasmid preparations"). Silica-slurry–purified DNA exhibits extremely high endotoxin levels. QIAGEN, QIAfilter, and HiSpeed Plasmid Kits and 2x CsCl ultracentrifugation yield very pure DNA with relatively low levels of endotoxin. EndoFree Plasmid Kits include an integrated endotoxin-removal step to yield plasmid DNA containing <0.1 EU/µg plasmid DNA.
QIAfilter Cartridges, provided in QIAfilter, HiSpeed, and EndoFree Plasmid Kits, are special filter units designed to replace centrifugation following alkaline lysis of bacterial cells. QIAfilter Cartridges completely remove SDS precipitates and clear bacterial lysates in a fraction of the time needed for centrifugation, reducing plasmid-purification time by up to 1 hour. QIAfilter Maxi Cartridges have a syringe-format and lysates are cleared in a matter of seconds by pushing the liquid through the filter. QIAfilter Mega-Giga Cartridges operate with house vacuum to efficiently clear even large volumes of bacterial lysate with minimal effort (please note that the bottle is not included in the kits).
The unique anion-exchange resin in QIAGEN-tips is developed exclusively for the purification of nucleic acids. Its exceptional separation properties result in DNA purity equivalent or superior to that obtained by two successive rounds of CsCl gradient centrifugation. Prepacked QIAGEN-tips operate by gravity flow and never run dry, minimizing the hands-on time required for plasmid preparation. The entire QIAGEN plasmid purification system avoids the use of toxic substances such as phenol, chloroform, ethidium bromide, and CsCl, minimizing hazard both to the user and the environment.
Endotoxins, also known as lipopolysaccharides or LPS, are cell-membrane components of Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli (see figure " Bacterial cell wall"). Endotoxins are released during the lysis step of plasmid purification and significantly reduce transfection efficiencies in endotoxin sensitive cell lines (see figures " Plasmid purification method versus transfection efficiency" and " Plasmid purity versus transfection efficiency" and tables "Endotoxin levels in plasmid preparations" and "EndoFree DNA yields high transfection efficiencies with primary cells"). Furthermore, endotoxins can influence the uptake of plasmid DNA in transfection experiments by competing with DNA for “free” transfection reagent. Endotoxins also induce nonspecific activation of immune responses in immune cells such as macrophages and B cells, which can lead to misinterpretation of transfection results. These responses include induced synthesis of proteins and lipids such as IL-1 and prostaglandin. Overall, endotoxins represent a noncontrollable variable in transfection experiment setup, influencing the outcome and reproducibility of results and making them difficult to compare and interpret. In gene therapy research, endotoxins can interfere by causing endotoxic-shock syndrome and activation of the complement cascade.
Features |
EndoFree Plasmid Maxi Kit |
EndoFree Plasmid Mega Kit |
EndoFree Plasmid Giga Kit |
| Applications | Research on gene therapy, transfection of sensitive cells | Research on gene therapy, transfection of sensitive cells | Research on gene therapy, transfection of sensitive cells |
| Culture volume/starting material | 100–250 ml culture volume | 500 ml – 2.5 liters culture volume | 2.5 liters culture volume |
| Plasmid type | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA | High-copy, low-copy, cosmid DNA |
| Processing | Manual (gravity flow) | Manual (gravity flow) | Manual (gravity flow) |
| Sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run | 1 sample per run |
| Time per run | 150 min | 220 min | 310 min |
| Yield | <500 µg | <2.5 mg | <10 mg |
Bacterial cells are lysed under alkaline conditions and the crude lysates are cleared using the QIAfilter Cartridge. At this stage, the Endotoxin Removal Buffer is added to the filtered lysate, which is incubated on ice. The cleared lysate is then loaded onto the anion-exchange tip where plasmid DNA selectively binds under appropriate low-salt and pH conditions. RNA, proteins, metabolites, and other low-molecular-weight impurities are removed by a medium-salt wash, and ultrapure plasmid DNA is eluted in high-salt buffer (see flowchart " QIAGEN Plasmid Kit procedures"). The DNA is concentrated and desalted by isopropanol precipitation and collected by centrifugation.
DNA purified with EndoFree Plasmid Kits is suitable for any sensitive application, including: